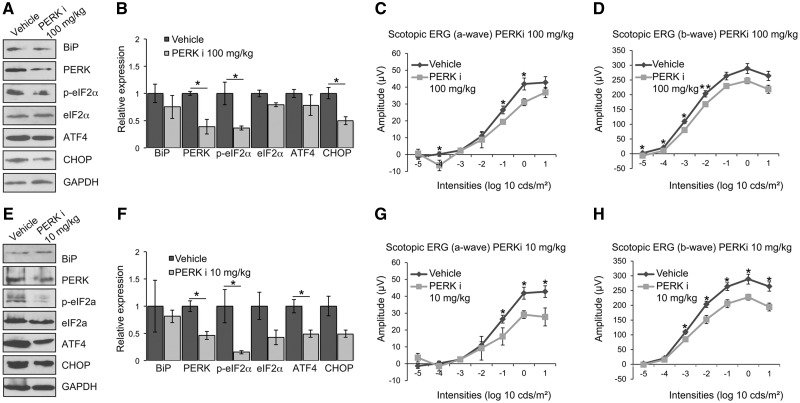
Figure 1.
PERK inhibition reduces visual responses in P23H-1 rats. P23H-1 rats were treated from P21-P35 with either GSK2606414A (PERKi) or vehicle. (A, E) Representative western blot of retina lysates of P36 P23H-1 rats treated with 100 mg/kg (A) or 10 mg/kg (E) PERKi or vehicle for BiP, PERK, p-eIF2α, eIF2α, ATF4 and CHOP. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B, F) Quantification of expression levels of BiP, PERK, p-eIF2α, total eIF2α, ATF4 and CHOP in P23H-1 rats after treatment with 100 mg/kg (B) or 10 mg/kg (F) PERKi. Densitometric analysis was used to calculate the levels of these proteins relative to vehicle; values are mean ± SEM n ≥ 4. (C, D) Scotopic ERG a-wave (C) and b-wave (D) amplitude results of P23H-1 rats (P36) treated from P21-P35 with either 100 mg/kg PERKi (n = 8) or vehicle (n = 6). (G, H) Scotopic ERG a-wave (G) and b-wave (H) amplitude results of P23H-1 rats (P36) treated from P21-P35 with either 10 mg/kg PERKi (n = 8) or vehicle (n = 6). Values are mean ± SEM, *P < 0.5, **P < 0.01, Student's t test.