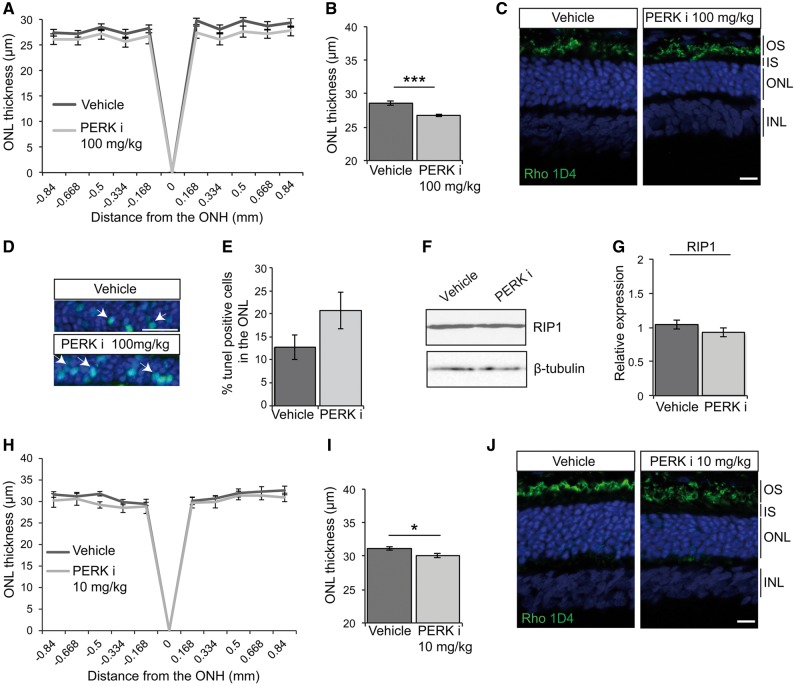
Figure 2.
PERK inhibition reduces photoreceptor survival in P23H-1 rats. P23H-1 rats were treated from P21-P35 with either 100 mg/kg (A–G) or 10 mg/kg (H–J) PERKi or vehicle. (A, H) Spider plot showing P23H-1 ONL thickness at P36 after PERKi (n = 6) or vehicle (n = 6) assessed by OCT. (B, I) Mean ONL thickness across the whole retina (E). Values are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test. (C, J) Representative images of the retina from P23H-1 (P36) rats treated with vehicle or PERKi. Cryosections were stained with anti-rhodopsin antibody 1D4 (green), and DAPI (blue) as indicated. (D, E) TUNEL staining in the ONL of P23H-1 rats treated with 100 mg/kg PERKi or vehicle treated. Arrows highlight positive TUNEL cells. Scale bar 10 µm. (D) Percentage of TUNEL positive cells in the ONL quantified by scoring n = 10 images each from 2 vehicle-treated rats and 2 PERKi-treated rats (100 mg/kg). Immunoblotting (F) and quantification (G) relative to vehicle of RIP1 immunoreactivity in PERKi (100mg/kg) and vehicle treated retinal lysates, β-tubulin was used as a loading control. Scale bar 20 µm.