Figure 7.
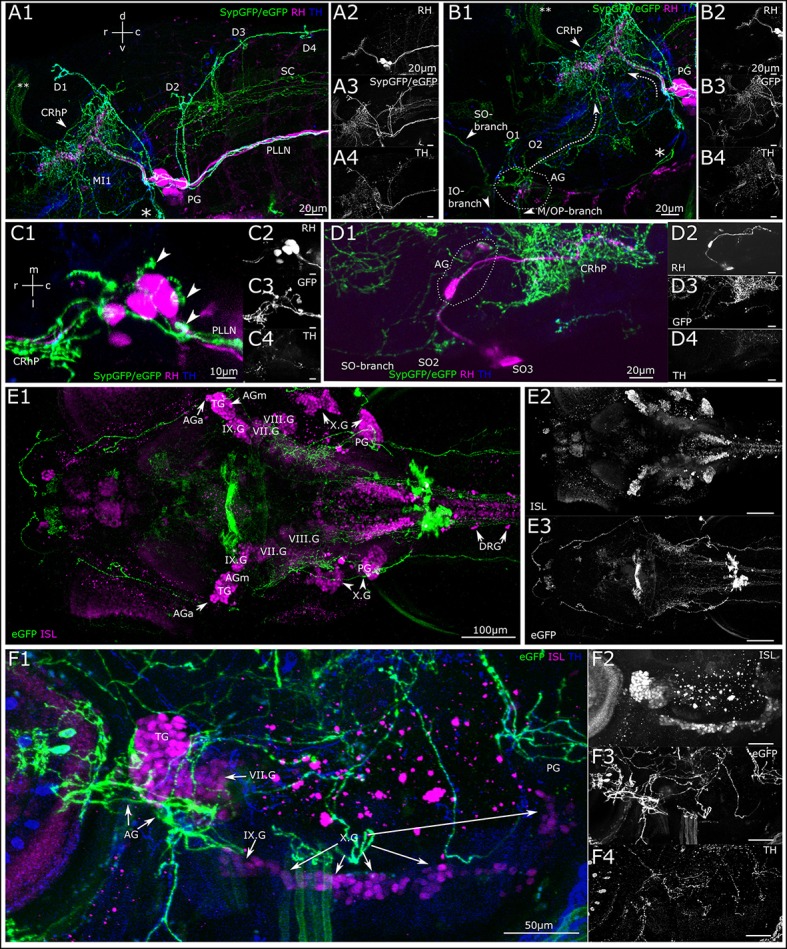
Dopaminergic projections to lateral line ganglia and other cranial ganglia. (A) Lateral view (MIP) of the region around the posterior lateral line ganglion (PG). Step size: 1 μm, total depth of: 81 μm. Primary afferent lateral line neurons retrogradely labeled with rhodamine dextran (A2, magenta in A1) by dye injection into the posterior lateral line nerve (PLLN) at a neuromast. A number of afferent neurons took up dye, which have cell bodies residing in the PG and project centrally into the rhombencephalon (CRhP, arrowhead). SypGFP/eGFP-CAAX labeling driven by th:Gal4-VP16 (A3, green in A1). DA-axons project through the PG and along the PLLN as well as to the dorsal (D) and otic (O) neuromasts. Ventrally, the projection branches toward the vagus ganglia (asterisk). Dorsally, the DA-projection runs parallel with the CRhP of the afferent neurons. Central DA-projections are present in the spinal cord (SC). Double asterisks: ectopically labeled commissure. TH-immunoreactivity of efferent DA-projections (A4, blue in A1). (B) Lateral view (MIP) of region around the anterior lateral line ganglion (AG), step size: 1 μm, total depth: 81 μm. Rhodamine was injected into the PLLN labeling afferent neurons of the posterior lateral line (B2, magenta in B1), but not of the anterior lateral line. DA-axons projecting through the AG labeled with th:Gal4-VP16 driven SypGFP/eGFP-CAAX (B3, green in B1), and projecting rostrally parallel to the infraorbital (IO) and supraorbital (SO) branch, as well as caudally (dotted arrow) toward the CRhP (arrow head) and ventrally to the mandibular (M) and opercular (OP) neuromasts. Asterisk marks the branch of the DA projection coming from the PG and running along the region of the vagus ganglia. Double asterisk: ectopically labeled commissure. TH-immunoreactivity labeling DA projections (B4, blue in B1). Orientation for A, B indicated in (A1). (C) Dorsal view (MIP) of PG. Pseudo-colors and channels as in (B). Step size: 1 μm, total depth: 59 μm. DA projections running through the PG. Arrowheads in C1 pointing to DA fibers projecting dorsally along the lateral line nerve branches toward the dorsal neuromasts. Rostrally, DA-projections run parallel with afferent neurons to CRhP. (D) Dorsal view (MIP) of region around AG. Rhodamine dextran (magenta in D1) was injected into the MI1/MI2 branch of the anterior lateral line and labels few afferent anterior lateral line neurons, which centrally project into the hindbrain, with efferent DA projection arborizing around the CRhP (green in D1). Step size: 1 μm, total depth: 155 μm. Orientation for (C,D), indicated in (C1). (E). Dorsal view (MIP) of whole mount, montage of two stitched tiles with larval head. Step size: 1 μm, total depth: 476 μm. Cell bodies of sensory afferent neurons are labeled with primary anti-Islet1/Islet2 (ISL), and secondary Alexa555 antibodies (E2, magenta in E1) in the cranial and dorsal root ganglia (AGa, anterior part of anterior lateral line ganglion; AGm, medial part of AG; TG, trigeminal ganglion; PG, posterior lateral line ganglion; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; VII.G, facial ganglion; VIII.G, statoacoustic ganglion; IX.G, glossopharyngeal ganglion; X.G, vagus ganglia). Th:Gal4 driven eGFP-CAAX labeling of DA-projections (E3). (F) Lateral view (MIP) of region with AG and PG. (step size, 3.63 μm, depth 137.9 μm). Pseudo coloring and channels as in (E). TH-immunoreactivity, (F4) and blue in (F1). DA projection contacting the AG and TG, and further projecting to the vagal ganglia.
