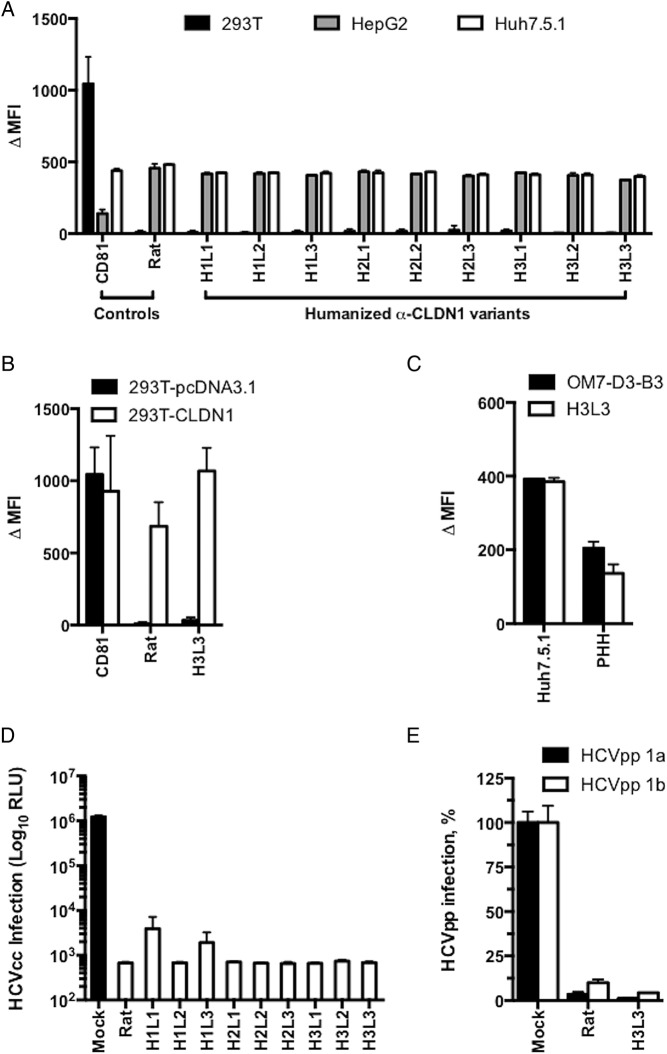
Figure 2.
Humanised anti-tight junction protein claudin-1 (CLDN1) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) specifically bind to CLDN1 and inhibit HCV infection. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of the binding of humanised OM-7D3-B3 anti-CLDN1 mAbs (20 µg/mL) to cell lines. Humanised antibodies specifically bind to Huh7.5.1 and HepG2 cells expressing human CLDN1 but not to 293T cells lacking CLDN1. Binding is expressed as delta median fluorescence intensity (ΔMFI) from one experiment performed in duplicate. (B) H3L3 specifically binds to exogenous CLDN1 expressed on the surface of 293T cells. CLDN-null 293T cells were transfected with either empty vector or CLDN1 prior to staining with isotype control, rat OM-7D3-B3 or humanised H3L3 antibody (20 µg/mL). The ΔMFI from one experiment performed in duplicate is shown. (C) H3L3 binds to primary human hepatocytes (PHH) with similar affinity as the parental rat antibody. PHH were stained with isotype control, rat OM-7D3-B3 or humanised H3L3 antibody (20 µg/mL). The ΔMFI from one experiment performed in duplicate are shown. (D) All humanised anti-CLDN1 mAbs inhibit HCVcc infection. Huh 7.5.1 cells were incubated with different mAbs (25 µg/mL) at 37°C for 1 hour prior to infection with HCVcc. Infectivity was assessed after 72 hours by measuring luciferase activity and is expressed as log relative luciferase units (RLU). (E) H3L3 inhibits entry of HCVpp bearing envelope glycoproteins of strains H77 (genotype 1a) and HCV-J (genotype 1b). PHH were treated with humanised antibody (20 µg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C prior to infection with HCVpp. Infectivity was measured by luciferase activity after 72 hours and is expressed as RLU. Graphs show results from one experiment performed in duplicate (A–C) or in triplicate (D and E).