Figure 2.
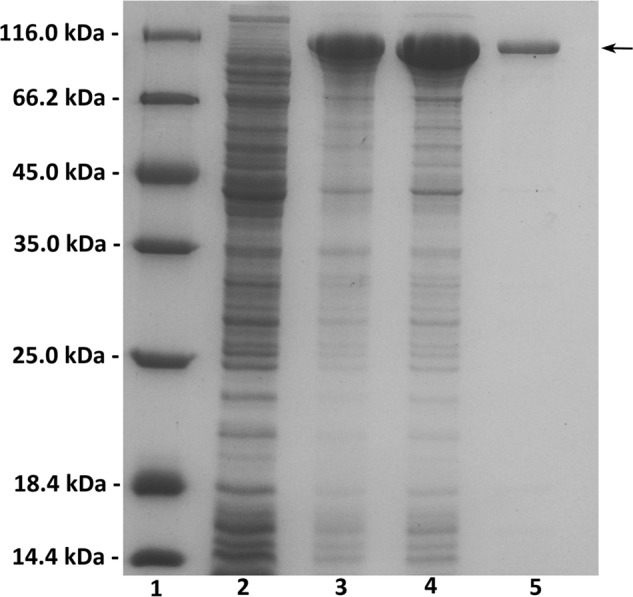
Purification of recombinant HCLase Er from E. coli by Ni2+-chelation chromatography. Enzyme purity following each fractionation step was assessed by SDS-PAGE using 13.2% polyacrylamide gels followed by staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Lane 1, unstained protein molecular weight marker SM 0431 (Thermo Fisher Scientific); lane 2, uninduced cell lysate; lane 3, induced cell lysate; lane 4, supernatant fluid of the induced cell lysate; lane 5, purified recombinant HCLase Er. Ten microliters of corresponding sample containing about 10 μg of protein was individually loaded on lanes 1–4, and 1 μg of purified enzyme was loaded on lane 5. Molecular mass markers and their corresponding masses are indicated.
