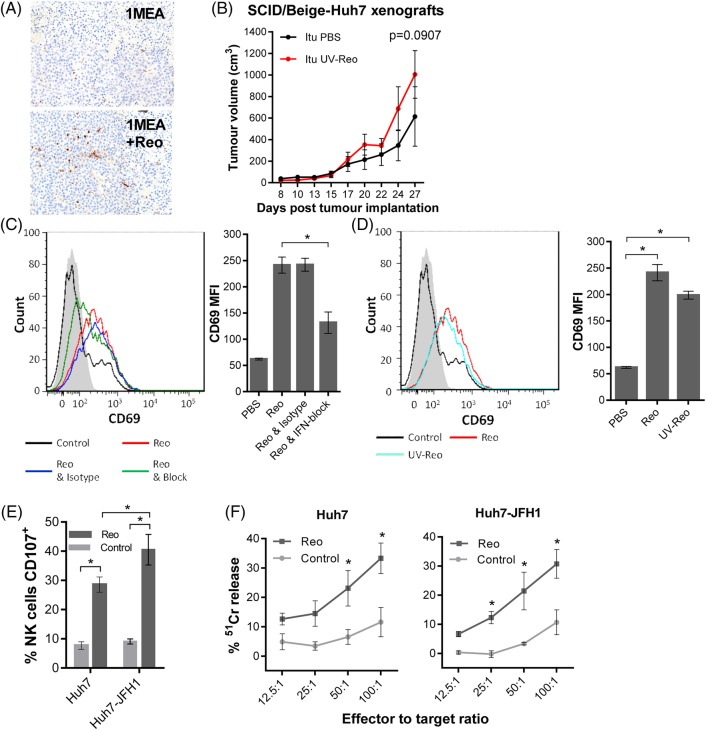
Figure 3.
Reo-stimulated interferon (IFN) drives anti-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) immune responses via natural killer (NK) cell activation. (A) Representative IHC staining (brown) for NK cells in 1MEA subcutaneous syngeneic tumours in BALB/c mice treated with 3 times weekly Itu injections of PBS or 1×106 PFU Reo. (B) Tumour growth of Huh7 subcutaneous xenografts in SCID/Beige mice treated with 3 times weekly Itu injections of PBS or 1×106 PFU uv-Reo. (C) Flow cytometry overlay plot (left) and quantification (right) of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) for NK CD69 expression within liver mononuclear cells (LMCs) treated using PBS, 1 PFU/cell Reo, 1 PFU/cell Reo and type I IFN blocking antibodies or 1 PFU/cell Reo and isotype antibodies. (D) Similar to (C), but LMCs were treated with PBS, 1 PFU/cell Reo or 1 PFU/cell uv-Reo. (E) Degranulation assay showing per cent CD107-positive liver NK cells. LMCs were pretreated with PBS or 1 PFU/cell Reo for 24 hours, then coincubated with Huh7 or Huh7-JFH1 targets for 4 hours. (F) 51Cr release assay using LMCs pretreated with PBS or 1 PFU/cell Reo for 24 hours, then washed and coincubated with 51Cr-labelled Huh7 or Huh7-JFH1 targets for 4 hours. Data are 51Cr release as a percentage of the potential maximum. *signifies p<0.005.