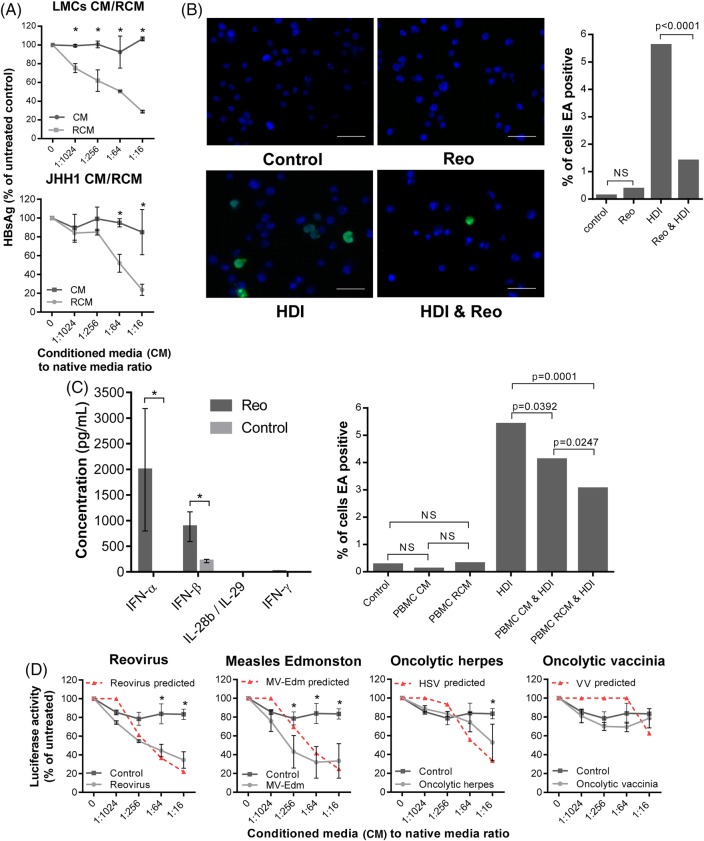
Figure 6.
Reo-induced antiviral responses inhibit HBV and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in vitro. (A) ELISA for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) secreted from PLC/PRF/5 cells treated for 5 days using a range of dilutions of conditioned media (CM) or reovirus-CM (RCM) derived from liver mononuclear cell (LMCs) (top) or JHH1 (bottom) cells. (B) Representative immunofluorescence (left) for EBV early antigen (EA) and quantification of EA-positive (right) Daudi cells. Cells were treated using PBS for 48 hours, 1 PFU/cell Reo for 48 hours, Histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDI) for 24 hours or 1 PFU/cell Reo for 48 hours followed by HDI for 24 hours. (C) (Left) ELISA for interferon (IFN)-α, IFN-β, IFN-γ and interleukin (IL)-28b/IL-29 derived from peripheral blood MC (PBMC) following stimulation with Reo or PBS control. (Right) Quantification of EA-positive Daudi cells treated for 24 hours using control media, PBMC CM, PBMC RCM, all followed by a further 24 hours treatment using either PBS or HDI. (D) Luciferase assay using Huh7-JFH1 cells treated for 24 hours with a range of dilutions of CM or 10 PFU/cell oncolytic virus (OV)-CM derived from mixed liver cells. * signifies p<0.005.