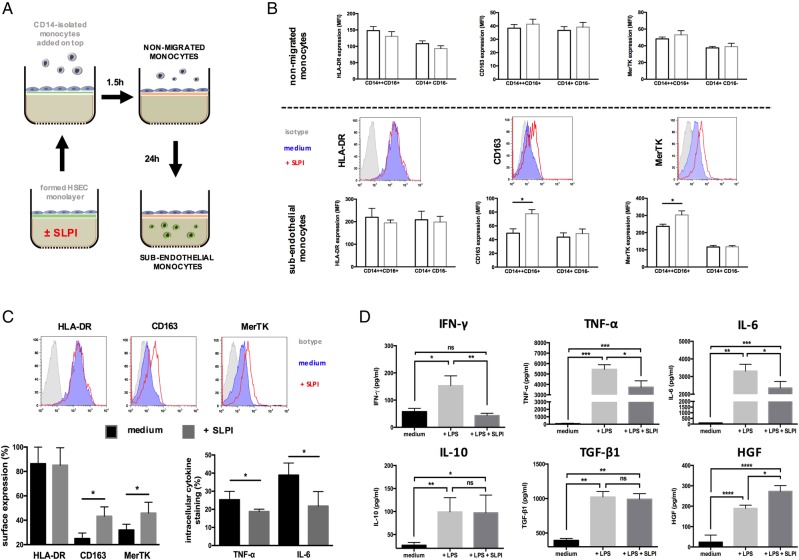
Figure 5.
Secretory leucocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) induces a Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK)highHLA-DRhigh phenotype in monocytes and liver-derived macrophages. (A–B) Effects of recombinant human (rh)-SLPI (0 and 0.5 µg/mL) on monocyte migration across hepatic endothelium were determined (n=3 independent experiments). (A) Schematic of migration assay: CD14-isolated monocytes are added on top of a preformed hepatic endothelium monolayer; non-migrated monocytes are harvested 1.5 hours after, while subendothelial monocytes are obtained 24 hours later. Phenotypic characterisation of non-migrated and subendothelial monocytes was determined by flow cytometry. (B) Data show HLA-DR, CD163 and MerTK expression levels and representative histograms (CD14++CD16+ subset) for (top panel) non-migrated and (lower panel) subendothelial monocytes. Results expressed as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (C and D) Effects of (rh)-SLPI (0 and 0.5 µg/mL) on hepatic macrophages isolated from normal liver explant tissue were assessed (n=5). (C) Data show representative histograms and surface marker expression in the CD14++CD16+ subset and intracellular cytokine levels in total monocytes following microbial challenge (LPS 100 ng/mL). (D) LPS-stimulated inflammatory cytokine levels (pg/mL) in hepatic mononuclear cell culture supernatants, as determined by ELISA. Non-parametric (Mann-Whitney) statistical analysis was used. Data presented as median values with IQR. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; iso, isotype control antibody; ns, non-significant; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.