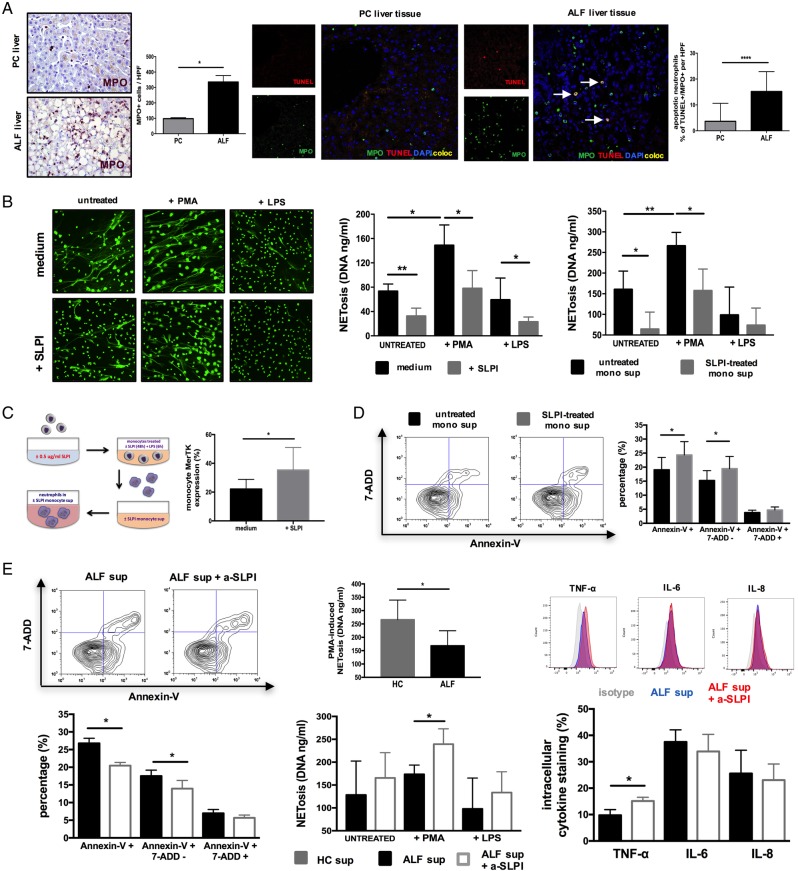
Figure 6.
Secretory leucocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) suppresses neutrophils through Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK)highHLA-DRhigh monocytes in a paracrine manner. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry (IHC) (left) and confocal (right) micrographs and enumeration of (MPO+) hepatic neutrophils and (MPO+TUNEL+) apoptotic neutrophils in centrilobular areas of pathological control (PC, n=4) and acute liver failure (ALF) (n=6) human liver tissue. IHC images (400×) show MPO+ (purple) cells. Confocal images show MPO (green), TUNEL (red), DAPI (blue) and coexpression (yellow) (400×). (B–E) Autocrine and paracrine effects of recombinant human (rh)-SLPI (0 and 0.5 μg/mL) on neutrophils were examined (n=5). (B) Neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis) was determined fluorometrically (DNA, ng/mL) in culture following stimulation with PMA (25nM) or LPS (100 ng/mL). (Left) Representative images of NETs using SYTOX Green Dye (1 μM). (Right) Data show NETosis (DNA, ng/mL) quantified in culture (1) with/without SLPI and (2) with ±SLPI-treated monocyte culture supernatants (n=3). (C) Paracrine experimental approach for neutrophils and data showing monocyte MerTK expression levels after culture with/without SLPI (48 hours). (D) Representative Annexin-V/7-AAD staining and percentage of apoptotic neutrophils in culture with ±SLPI-treated monocyte supernatants (n=5). (E) SLPI paracrine effects were assessed by blocking SLPI's activity on monocytes in ALF plasma (α-SLPI, 5 µg/mL) (n=5). (Left) Representative Annexin-V/7-AAD staining and percentage of apoptotic neutrophils; (middle) NET formation (DNA, ng/mL) and (right) LPS-stimulated (100 ng/mL) intracellular cytokine levels of neutrophils (n=5 each). Data presented as median values with IQR. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. HC, healthy controls; IL, interleukin; ns, non-significant; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.