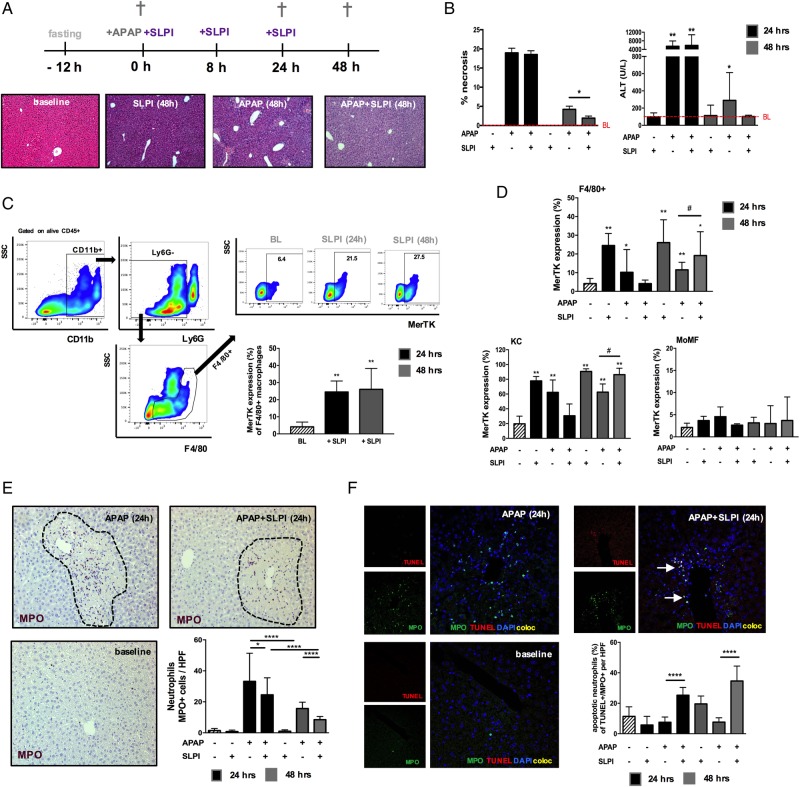
Figure 8.
Secretory Leucocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) administration in wild-type (WT) mice induces Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK)+ macrophages and promotes hepatic resolution following APAP-induced acute liver injury. WT mice were dosed with SLPI (−/+) or APAP (+/−) or APAP plus SLPI (+/+) while untreated mice (−/−) served as baseline controls (n=6/group). Mice were studied at baseline (white bars), 24 hours (black bars) and 48 hours (grey bars). (A) Schematic describes the experimental dosing and representative images of H&E-stained livers (baseline and 48 hours). (B) Quantification of necrosis and plasma alanine transaminase (ALT) levels. (C) Representative flow cytometry analysis and data show MerTK expression of F4/80+ macrophages at baseline and following SLPI administration. (D) Data show MerTK expression levels of F4/80+ macrophages, subanalysed into (CD11blowF4/80high)-resident Kupffer cells (KC) and (CD11bhighF4/80low) monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMF). (E) Representative liver immunohistochemistry images at baseline and 24 hours (n=5 each) and enumeration of MPO+ (purple) hepatic neutrophils (200×). (F) Representative liver confocal micrographs at baseline and 24 hours (n=5 each) stained for MPO (green), TUNEL (red), DAPI (blue); coexpression (yellow) (400×). Data show the percentage of (MPO+TUNEL+) apoptotic neutrophils. Non-parametric (Mann-Whitney) statistical analysis was used. Data are presented as median values with IQR. * or #p<0.05, **p<0.01, **** p<0.0001. SSC, side scatter.