Table 2. Monomer variations a .
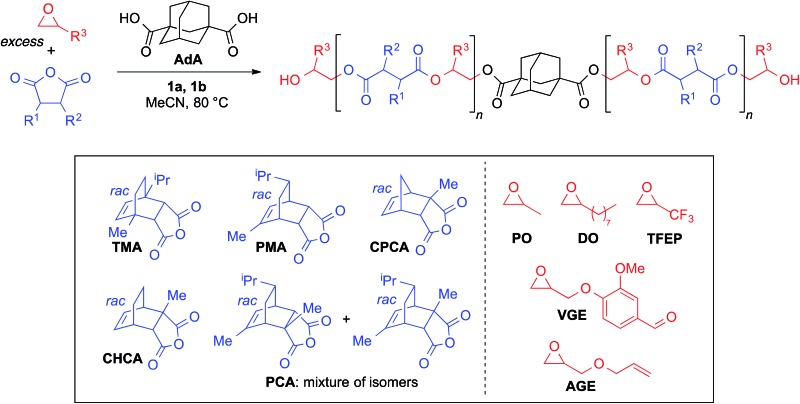
| ||||||
| Entry | Epoxide | Anhyd. | t rxn (h) | Conv. b (%) | M n c (kDa) | Đ c |
| 1 | PO | CPCA | 5.0 | >99 | 7.1 | 1.04 |
| 2 | PO | PMA | 4.5 | >99 | 9.3 | 1.04 |
| 3 | PO | TMA | 5.3 | >99 | 6.9 | 1.04 |
| 4 d | PO | TMA | 11.0 | 95 | 20.0 | 1.04 |
| 5 | PO | PCA | 8.0 | >99 | 7.5 | 1.05 |
| 6 | PO | CHCA | 5.5 | >99 | 6.7 | 1.04 |
| 7 | DO | CPCA | 24.5 | >99 | 9.2 | 1.08 |
| 8 e | VGE\PO | CPCA | 5.0 | >99 | 7.9 | 1.06 |
| 9 | AGE | PMA | 7.5 | >99 | 8.5 | 1.10 |
| 10 | TFEP | CPCA | 23.0 | >99 | 8.8 | 1.07 |
a[Epox.] : [Anhyd.] : [1a] : [1b] : [AdA] = 2000 : 400 : 1 : 0.9 : 5 VPO = 0.9 mL VMeCN = 0.6 mL MeCN was added solely as a the solvent in the stock solutions of 1a and 1b that were used.
bConversion of anhydride determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy.
cDetermined by GPC in THF relative to polystyrene standards.
d[PO] : [TMA] : [1a] : [1b] : [AdA] = 4000 : 1200 : 1 : 0.9 : 5 VPO = 1.8 mL VMeCN = 0.6 mL MeCN was added solely as the solvent in the stock solutions of 1a and 1b that were used.
e100 equiv. VGE and 2000 equiv. PO. 1H NMR analysis showed that the polymer was 12% poly(VGE-alt-CPCA) and 88% poly(PO-alt-CPCA).
