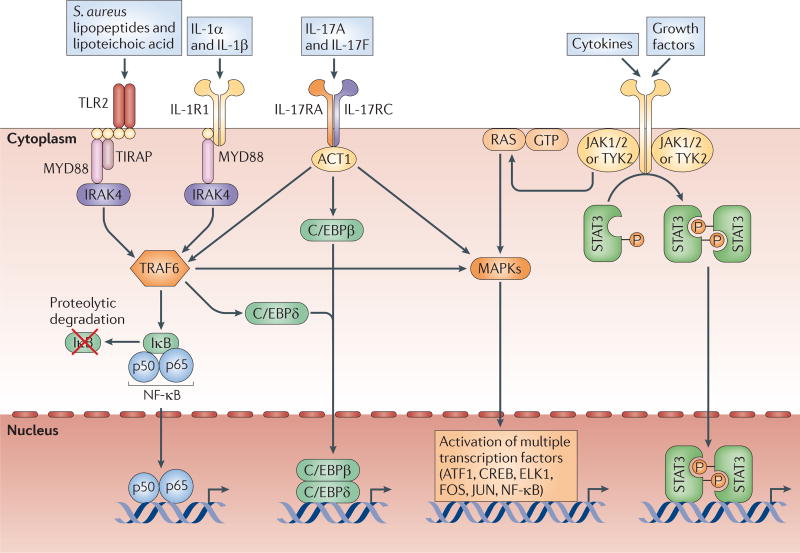
Figure 2. Major host cell signalling pathways involved in the immune response against S. aureus cutaneous infections.
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), which is activated by Staphylococcus aureus lipopeptides and lipoteichoic acid, and interleukin-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1), which is activated by IL-1α and IL-1β, both signal through the adaptor molecule MYD88 (myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88). MYD88 triggers the activation of IRAK4 (IL-1R-associated kinase 4) and TRAF6 (TNFR-associated factor 6), leading to the activation of NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB), C/EBPβ/δ (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-β/δ) and MAPKs (mitogen-activated protein kinases, such as JNK (JUN N-terminal kinase), p38 and ERK1 (extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1) or ERK2). TLR2 also uses TIRAP (TIR domain-containing adaptor protein) to initiate signalling. The IL-17RA–IL-17RC complex, which is expressed mainly on epithelial cells, is activated by IL-17A and IL-17F homodimers or heterodimers and uses ACT1 (NF-κB activator 1) to activate similar pathways to MYD88. STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) is a transcription factor that is activated downstream of various cytokine (IL-6, IL-10, IL-11, IL-19, IL-21, IL-22, IL-23, IL-24, IL-25, IL-26, IL-27 and IL-35) receptors and growth factor receptors (EGFR, FGFR, IGFR, HER2, HGFR, PDGFR, VEGFR and GCSFR). Each of these signalling pathways leads to the activation of transcription factors that alone or in combination promote the transcription of pro-inflammatory mediators involved in the immune response against S. aureus. ATF1, activating transcription factor 1; CREB, cAMP-responsive element-binding protein; ELK1, ETS-like protein 1; IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; JAK, Janus kinase; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2.