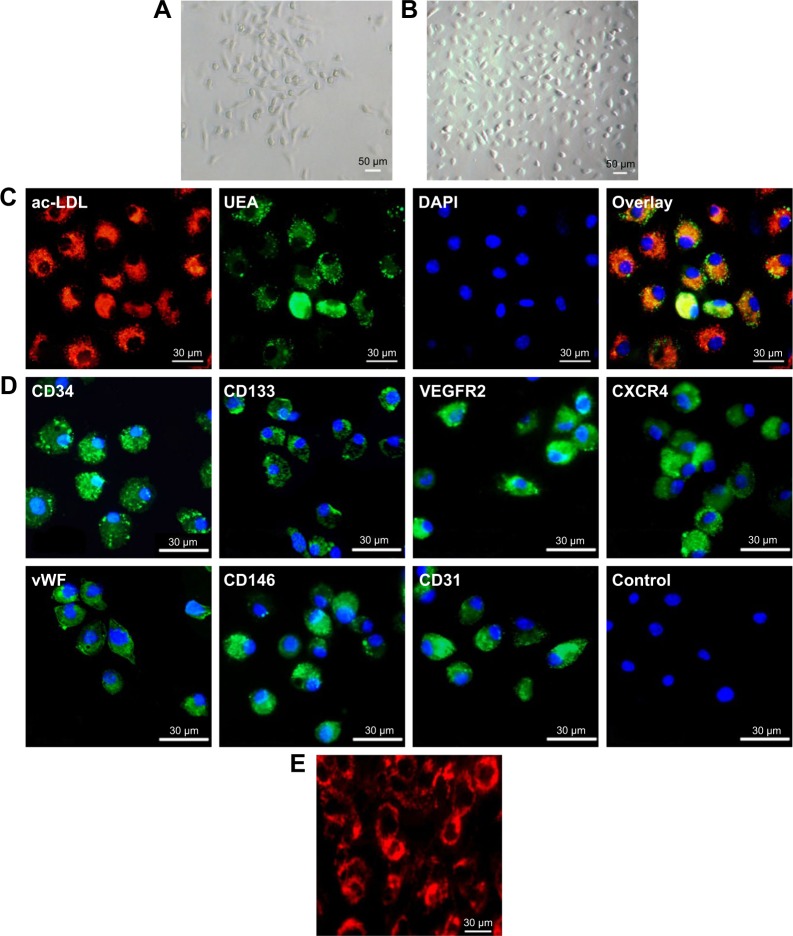
Figure 2.
Morphological and immunocytochemical analyses of mouse bone marrow-derived EPCs. (A) The shape of mononuclear cells was thin and flat on day 3, and a round and fusiform appearance was subsequently observed on day 7 (magnification ×100). (B) On day 14, the cells exhibited a typical fusiform or “cobblestone” morphology (magnification ×100). (C) Uptake of Dil-labeled acLDL and binding of endothelial-specific fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled lectin in EPCs in culture for 14 days (magnification ×400). Lectin and lipoprotein positivity colocalized in >95% of cells. (D) Immunocytochemical images of cells showing positive staining for the CD34, CD133, VEGF receptor 2, CXCR4, vWF, CD146 and CD31 markers. (E) Fluorescence image showing the uptake of multimodal imaging of bCD-PLL by EPCs (day 14) with positive rhodamine signals (magnification ×400).
Abbreviations: EPC, endothelial progenitor cell; acLDL, acetylated low-density lipoprotein; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor 4; vWF, von Willebrand factor; bCD, bacterial cytosine deaminase; PLL, poly-L-lysine; UEA, Ulex europaeus agglutinin-1; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; VEGFR2, VEGF receptor 2.