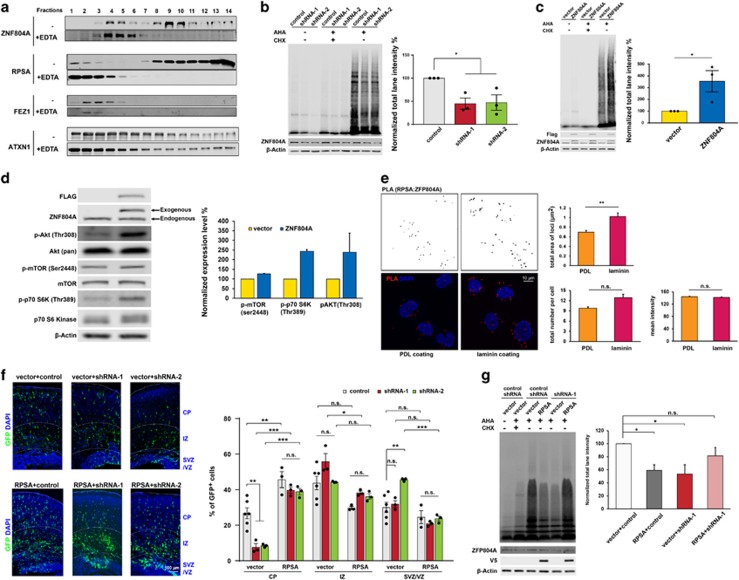
Figure 4.
ZNF804A controls protein translation efficiency. (a) ZNF804A sedimented in two fractions of polyribosomes prepared from HEK293 cells. EDTA treatment disassociated ZNF804A from the high-to-low molecular mass fractions. (b) AHA-labeled nascent proteins decrease with Zfp804a shRNAs in mouse CAD cells. n=3 for each group, *P<0.05, mean±s.e.m., t-tests. (c) AHA-labeled nascent proteins increase with ZNF804A overexpression in mouse CAD cells. n=3 for each group, *P<0.05, mean±s.e.m., t-tests. (d) ZNF804A overexpression increases phosphorylation of AKT, mTOR and p70 S6K. n=2, mean±s.e.m. (e) Laminin stimulates ZNF804A and RPSA interaction. Duolink assay detects close interaction of ZNF804A and RPSA in response to PDL and laminin. Quantifications show total area of the loci (unit= μm2), total number of loci each cell, and mean intensity (AU). n=99 for PDL coating and n=107 for laminin coating, **P<0.01, mean±s.e.m., Mann–Whitney U-test. Scale bar, 10 μm. (f) Co-electroporation of RPSA with Zfp804a shRNAs in E14.5 embryonic brain rescues the migration deficit caused by ZNF804A knockdown. Percentage of GFP cells in each region. n=6 for vector+control and n=3 for other groups, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, mean ±s.e.m., one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test. Scale bar, 100 μm. (g) Deficiency of AHA-labeled nascent protein caused by Zfp804a shRNAs can be rescued by RPSA in mouse CAD cells. n=5, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, mean±s.e.m., one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test. AHA, azidohomoalanine; ANOVA, analysis of variance; AU, arbitrary unit; GFP, green fluorescent protein; n.s., not siginificant PDL, poly-d-lysine.