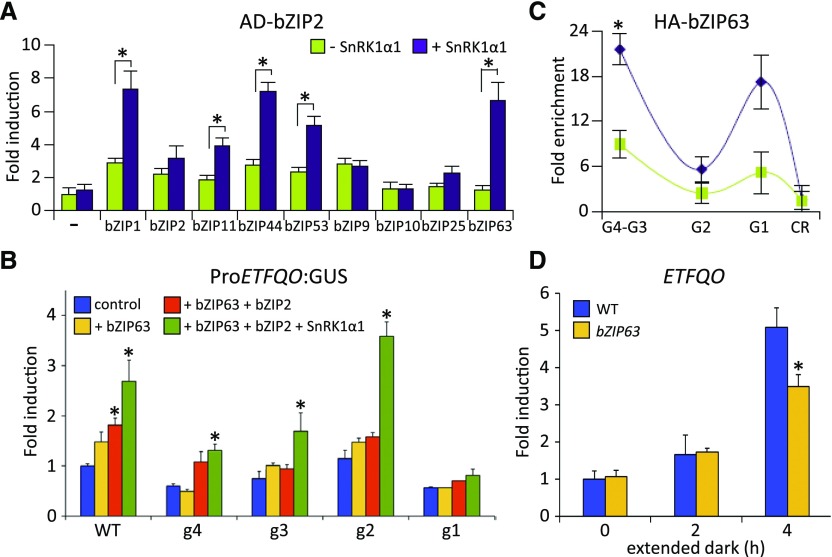
Figure 4.
Regulation of the ETFQO Gene by bZIP Dimers of Group C and S1.
(A) P2H assays. Changes in the dimerization properties of BD-bZIP2 with AD-fusions of the bZIP TFs indicated (green), depending on coexpression with SnRK1α1 (purple). Given are mean values (±sd; leaf-derived protoplasts, n = 3) relative to transfections with reporter only (–), Student’s t test, *P < 0.05. BD, Gal4-DNA binding domain; AD, Gal4-DNA activation domain.
(B) Activation of mutated versions (g1–g4) of the ProETFQO:GUS reporter by HA-bZIP63 (yellow), HA-bZIP2 + HA-bZIP63 (orange), and HA-bZIP2 + HA-bZIP63 + SnRK1α1 (green). Given values are mean values (±sd; n = 3) relative to transfections with reporter vector only (control, blue). Student’s t test, *P < 0.05.
(C) ChIP-PCR of HA-bZIP63 in Arabidopsis protoplasts using the indicated ETFQO-specific primers and an α-HA-specific antibody to detect binding at the G-boxes G1-G4. CR: control corresponding to the coding region. Given values are mean values (±sd; n = 3) relative to enrichment of the control region, Student’s t test, *P < 0.01.
(D) RT-qPCR analysis of ETFQO expression in the wild type and bzip63 after extended darkness for the time points indicated (n = 3). Student’s t test of the wild type at the respective time points, *P < 0.05.