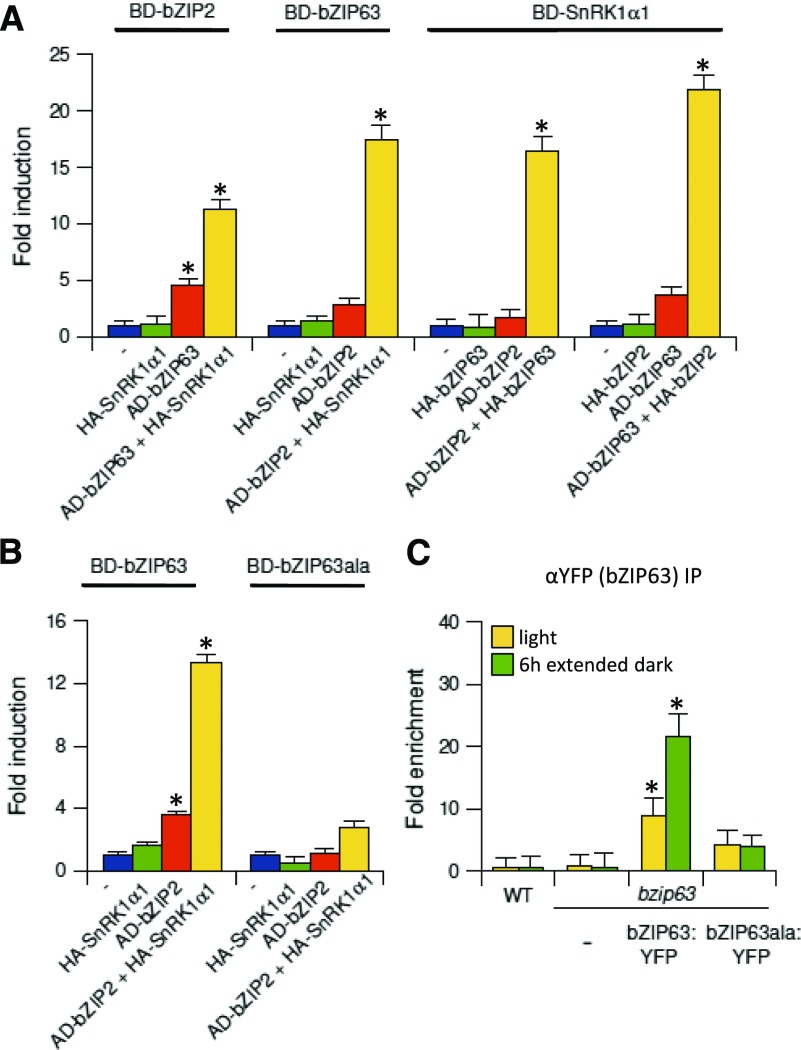
Figure 5.
Complex Formation between SnRK1α1, bZIP2, and bZIP63.
(A) P3H assay. Interaction between the BD- and AD-fused proteins indicated in the presence or absence of the third partner (HA-fusion protein).
(B) P3H assay. Interaction between AD-bZIP2 with BD-bZIP63 or BD-bzip63ala (S/A exchange mutant of the SnRK1-specific phosphorylation sites: S29/294/300A). Values are calculated as fold induction relative to transfections with the reporter plasmid only (–) (mean values ± sd, n = 3; Student’s t test of promoter background activity, *P < 0.05).
(C) ChIP-PCR in 4-week-old bzip63 knockout (Ws) plants and lines complemented with bZIP63:YFP or bZIP63ala:YFP under the control of the endogenous promoter. Specific primers detecting the G3-G4 site on the ETFQO promoter and an αGFP-antibody were used. Plant material was harvested after 6 h in the light (yellow) or 6 h in extended darkness (green). Given is fold enrichment (mean values ± sd, n = 3) relative to the wild type in the light. Student’s t test of the wild type in light, *P < 0.05.