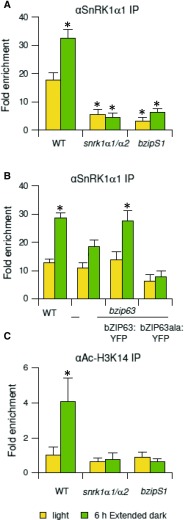
Figure 6.
Recruitment of SnRK1 to the ETFQO Promoter.
(A) ChIP-PCR of SnRK1α1 in wild-type, snrk1α1/α2 and bzipS1 plants using primers amplifying the G3-G4 site of the ETFQO promoter and an SnRK1α1-specific antibody.
(B) ChIP-PCR of SnRK1α1 in wild type, bzip63 mutant, and bzip63 complemented with a genomic bZIP63 fragment fused to YFP (bZIP63:YFP) (all ecotype Ws) or the corresponding construct carrying S/A exchange mutations in the SnRK1-specific phosphorylation sites (bZIP63ala:YFP) using an SnRK1α1-specific antibody.
(C) Acetylation of the ETFQO promoter. ChIP-PCR using an Ac-H3K14 antibody. All analyses are performed using three biological replicates of 3-week-old rosette leaves in the light (yellow) or 6 h extended darkness (green). Given are mean values (±sd) calculated relative to the input in the light (set to 1). Student’s t test of wild-type samples in light, *P < 0.05.