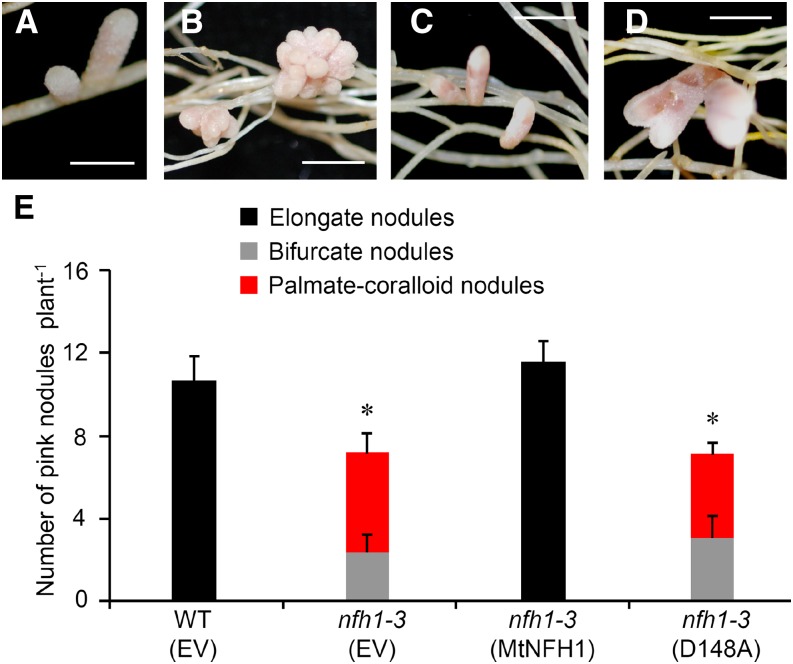
Figure 8.
Expression of MtNFH1 and MtNFH1(D148A) in the nfh1-3 Mutant.
Roots of the nfh1-3 mutant plants were transformed with the MtNFH1pro-MtNFH1 or MtNFH1pro-MtNFH1(D148A) construct. For comparison, wild-type (R108) plants and the nfh1-3 mutant were transformed with the empty vector pCAMBIA1302. Plants with transgenic roots were then inoculated with S. meliloti Rm41. Nodule formation was analyzed at 20 dpi.
(A) Elongate nodules formed on wild-type roots transformed with the empty vector.
(B) Palmate-coralloid nodules formed on nfh1-3 roots transformed with the empty vector.
(C) Elongate nodules formed on nfh1-3 roots transformed with MtNFH1pro-MtNFH1.
(D) Palmate-coralloid nodules formed on nfh1-3 roots transformed with MtNFH1pro-MtNFH1(D148A).
(E) Quantification of different types of nodules. Data from individually analyzed plants (n ≥ 12) indicate means (±se). The nfh1-3 mutant transformed with the empty vector or the MtNFH1pro-MtNFH1(D148A) construct formed fewer nodules than wild-type plants transformed with the empty vector (asterisks; Kruskal-Wallis test, P ≤ 0.05; Supplemental File 1).
EV, empty vector; MtNFH1, transformed with MtNFH1pro-MtNFH1; D148A, transformed with MtNFH1pro-MtNFH1(D148A). Bars = 2 mm.