Figure 5.
ARF3 Directly Represses AHK4 to Regulate FM Determinacy.
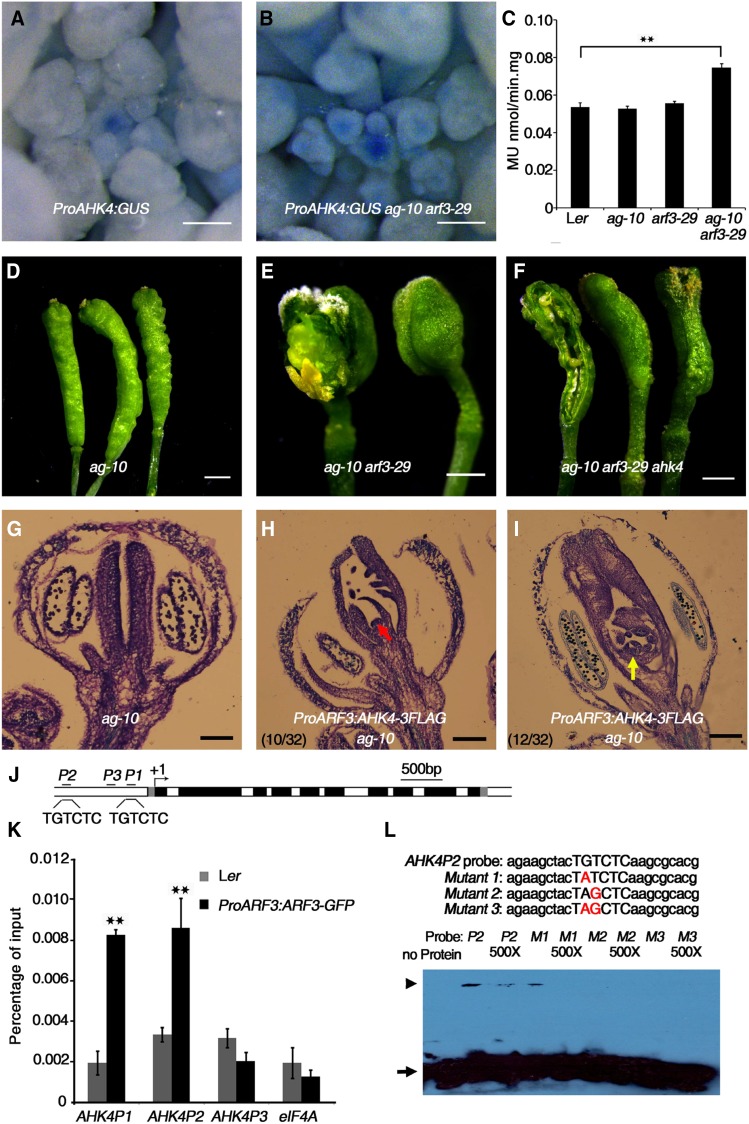
(A) and (B) Expression of ProAHK4:GUS in Ler (A) and arf3-29 (B) inflorescences under the same staining conditions. The stronger GUS staining in arf3-29 compared with Ler indicates that AHK4 expression was derepressed in arf3-29.
(C) Quantitative GUS activity in inflorescences of the indicated plants. Mean values of three biological replicates with independently prepared inflorescence materials containing unopened flowers are shown. **P < 0.01 (Student’s t test).
(D) to (F) Representative silique phenotypes of ag-10 (D), ag-10 arf3-29 (E), and ag-10 arf3-29 ahk4 (F). In (E) and (F), the leftmost silique has one carpel of the primary gynoecium removed to show the structures contained therein. The ahk4 mutation partially rescued the severe FM determinacy defect of ag-10 arf3-29.
(G) to (I) Longitudinal sections of representative siliques of the following: ag-10 (G) and ProARF3:AHK4-3FLAG ag-10 with severe (H) and intermediate (I) FM indeterminacy. Increased AHK4 gene expression in ARF3 expression regions resulted in severe FM determinacy defects in 10 out of 32 plants, as characterized by a sustained FM (red arrow in [H]), and intermediate FM indeterminacy in 12 out of 32 plants, as indicated by excess tissues growing within the primary ovary (yellow arrow in [I]).
(J) Diagram of the AHK4 genomic region, with the arrow indicating the transcription start site (+1). Dark-gray rectangles, untranslated regions; black rectangles, exons; white rectangles, introns. Black bold lines with P1, P2, and P3 indicate fragments examined by ChIP-qPCR. “TGTCTC” is the typical ARF binding motif. Bar = 500 bp.
(K) ChIP assay with anti-GFP antibody to examine ARF3 binding at AHK4 in Ler and ProARF3:ARF3-GFP arf3-29 inflorescences. The regions marked in Figure 5J were examined. ARF3 could bind the P1 and P2 regions containing the “TGTCTC” motif but not the P3 region. eIF4A served as a negative control. Error bars represent the sd from three biological repeats with independently prepared inflorescence materials containing unopened flowers. **P < 0.01 (Student’s t test) between Ler and ProARF3:ARF3-GFP arf3-29 inflorescences.
(L) EMSA confirmation of ARF3-GST binding to the AHK4 P2 region. Upper panel: native and mutated AHK4P2 sequence used for the EMSA. The mutated nucleotides are shown in red. The arrowhead indicates band shifts (complexes of ARF3-GST protein and probe DNA), and the arrow indicates free probe. Nonlabeled oligonucleotides were used as a competitor.
Bars = 100 µm in (A) and (B), 1 mm in (D) to (F), and 50 µm in (G) to (I).