Fig. 6.
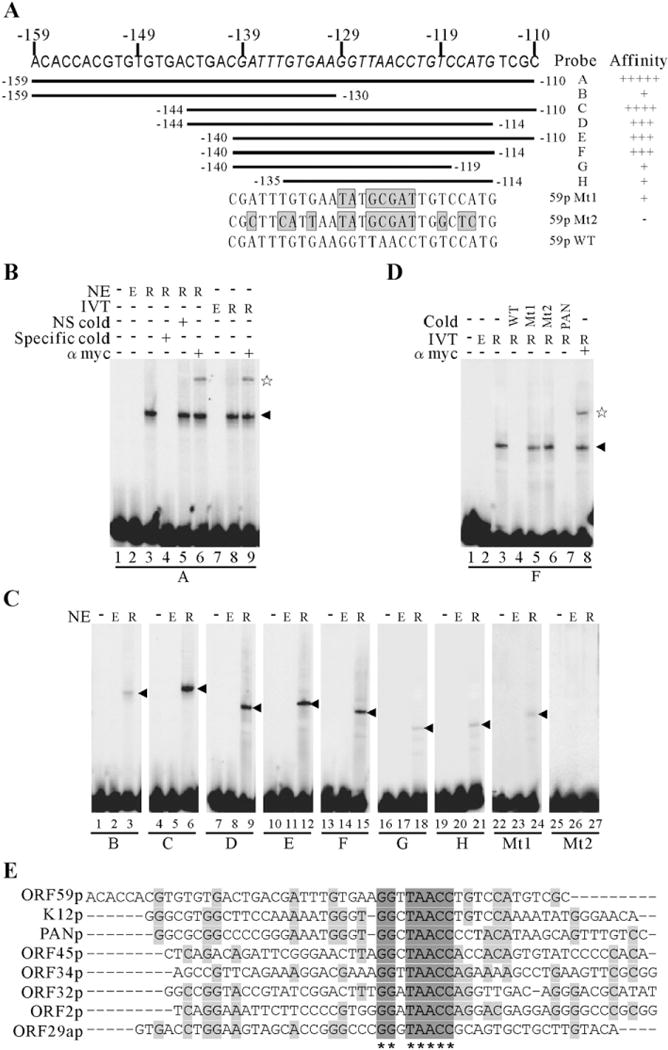
RTA directly binds to the 59pRRE in vitro and mapping of the core ORF59 RRE and the conservation of consensus binding sequences in other promoters. (A) Schematic representation of the oligonucleotides tested for RTA binding by EMSAs. Nucleotide residues of the 27-bp core RRE are italicized and the mutated minimal 59pRREs are shown at the bottom. The grey boxes correspond to the mutation sites. (B) EMSA of probe A with either overexpressed nuclear extracts (lanes 3 to 6) or in vitro translated recombinant Myc-RTA protein (lanes 8, 9). A 50-fold excess of unlabeled specific competitors (lane 4) and a nonspecific competitor (lane 5) was incubated in the presence of recombinant Myc-RTA protein for the competition assay. The RTA-bound complexes were supershifted by a monoclonal anti-Myc-tag antibody (lanes 6, 9). (C) Wild type oligonucleotides B to H and mutated ones were labeled and incubated in the absence or presence of nuclear extracts from empty vector or RTA expression vector transfected 293T cells, and their relative binding affinities are summarized and shown in the right of (A). (D) The specificity of the binding complex formed by 59pF and RTA. 59pF were end-labeled and incubated with in vitro translated Myc-tagged RTA protein. Competition assays were performed by inclusion 50-fold excess of unlabeled specific competitors 59pF (lane 4) or mutated 59pF (lanes 5 and 6) or PANpRRE (lane 7) in the binding reactions before incubation with 1-fold of radiolabeled probe 59pF. The specific binding complex was supershifted by a monoclonal anti-Myc-tag antibody (lane 8). The arrowhead denotes the specific binding of RTA to DNA and the pentagram denotes the supershift. NE, nuclear extracts; IVT, in vitro translated; NS, nonspecific; Mt, mutated 59pRRE; E, empty vector; R, RTA expression vector. (E) The alignment depicts the conservation of consensus binding sequences (GGNTAACC) in other KSHV promoters.
