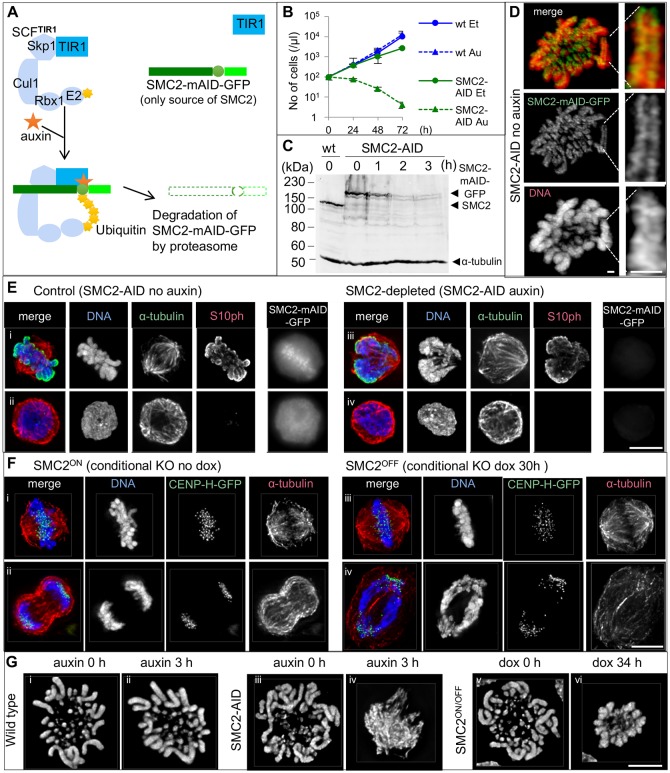
Fig. 1.
Rapid depletion of SMC2–mAID–GFP upon auxin treatment results in a severely defective mitotic chromosome formation. (A) Diagram introducing SMC2-AID cells. Auxin addition recruits the mAID tag to the SCFTIR1 complex, resulting in rapid degradation of SMC2–mAID–GFP via the proteasome pathway. (B) Growth curve of wild-type (wt) cells and SMC2-AID cells treated with either ethanol (Et, solvent) or 125 µM auxin (Au). Data are plotted as mean±s.d. (n=4). (C) Immunoblot analysis of asynchronous wild-type and SMC2-AID cells. SMC2-AID cells were treated with 125 µM auxin for 0–3 h. SMC2 and SMC2–mAID–GFP were detected with an anti-SMC2 antibody. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (D) Live-cell imaging of a SMC2-AID cell with a Zeiss Airyscan microscope. DNA was stained with SiR-DNA. SMC2–mAID–GFP concentrated along the axis of sister chromatids. Scale bars: 1 µm. (E) SMC2-AID cells treated with ethanol (solvent) (i,ii) or auxin for 3 h (iii,iv) were fixed with 4% formaldehyde, and stained for α-tubulin (green), H3S10ph (red) and DNA (blue). The GFP signal was undetectable (iii,iv) and the shape of mitotic chromosomes (iii) was highly abnormal in SMC2-depleted cells. Scale bar: 5 µm. (F) SMC2ON/OFF/CENP-H–GFP cells (Vagnarelli et al., 2006) converted into CDK1as were treated with doxycycline for 0 or 30 h, and stained in metaphase and anaphase for DNA (blue), CENP-H–GFP (green) and α-tubulin (red). (G) Wild-type/CDK1as cells (0 or 3 h auxin treatment), SMC2-AID/CDK1as cells (0 or 3 h auxin treatment) cells and SMC2ON/OFF/CDK1as cells (0 or 34 h doxycycline treatment) were fixed with cold methanol/acetic acid and stained for DNA. More examples are shown in Fig. S1B. Scale bars: 5 µm.