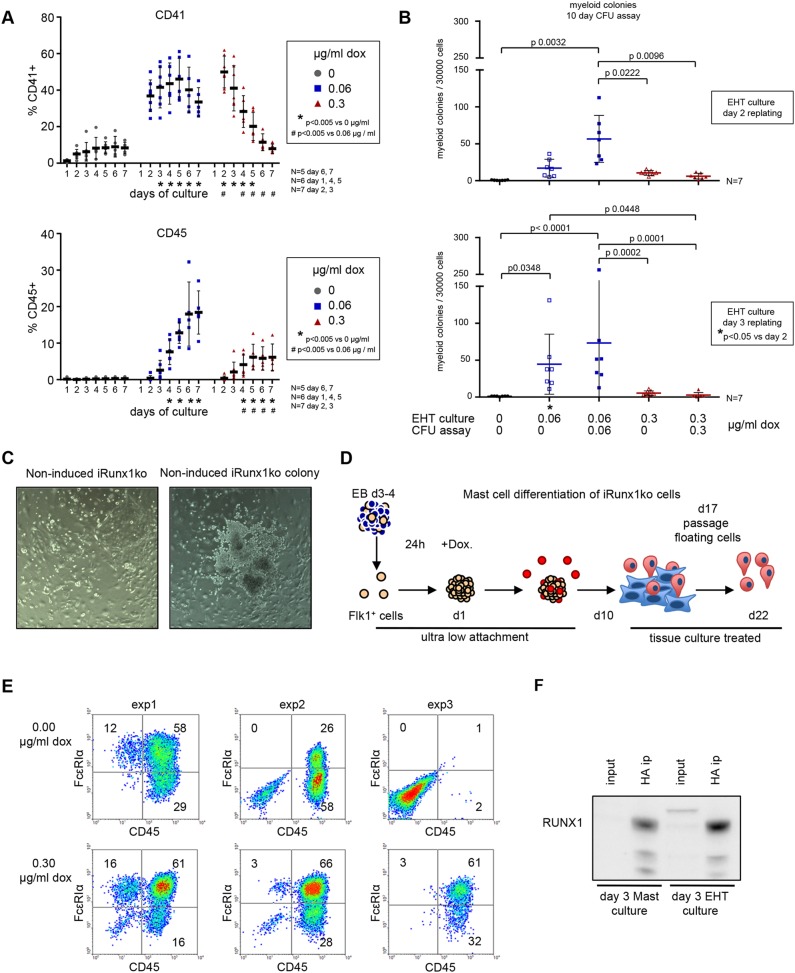
Fig. 3.
High Runx1 induction in iRunx1ko hampers hematopoietic potential. (A) Flow cytometry time course depicting the percentage of CD41+ (top) and CD45+ (bottom) cells in iRunx1ko upon doxycycline induction. Individual biological experiments and mean±s.d. are shown. Two-way ANOVA. N=biological replicates. (B) Myeloid hematopoietic colony-formation assay with iRunx1ko re-plated after 2 (top) or 3 (bottom) days of EHT culture. Individual biological experiments and mean±s.d. are shown. Two-way ANOVA. N=biological replicates. (C) iRunx1ko day 3 EHT-cultures cultured for 5 days in liquid hematopoietic mix. Right-hand panel shows a rare colony of budding cells in non-induced iRunx1ko cells. (D) Schematic of mast cell differentiation. FLK1+ cells were re-plated in mast cell media under ultra-low-attachment conditions. One day after re-plating, the cells were induced with doxycycline. Mast assays were analyzed after 22 days of culture. (E) Flow cytometry analysis of three independent iRunx1ko mast assays with or without doxycycline. In two out of three experiments, CD45+ cells could be generated in the absence of doxycycline induction. (F) RUNX1 western blot on day 3 non-induced iRunx1ko mast and EHT culture HA-tag immunoprecipitations. Input represents 5% of the total lysates. HA antibody raised in mouse, RUNX1 antibody raised in rabbit.