Fig. 1.
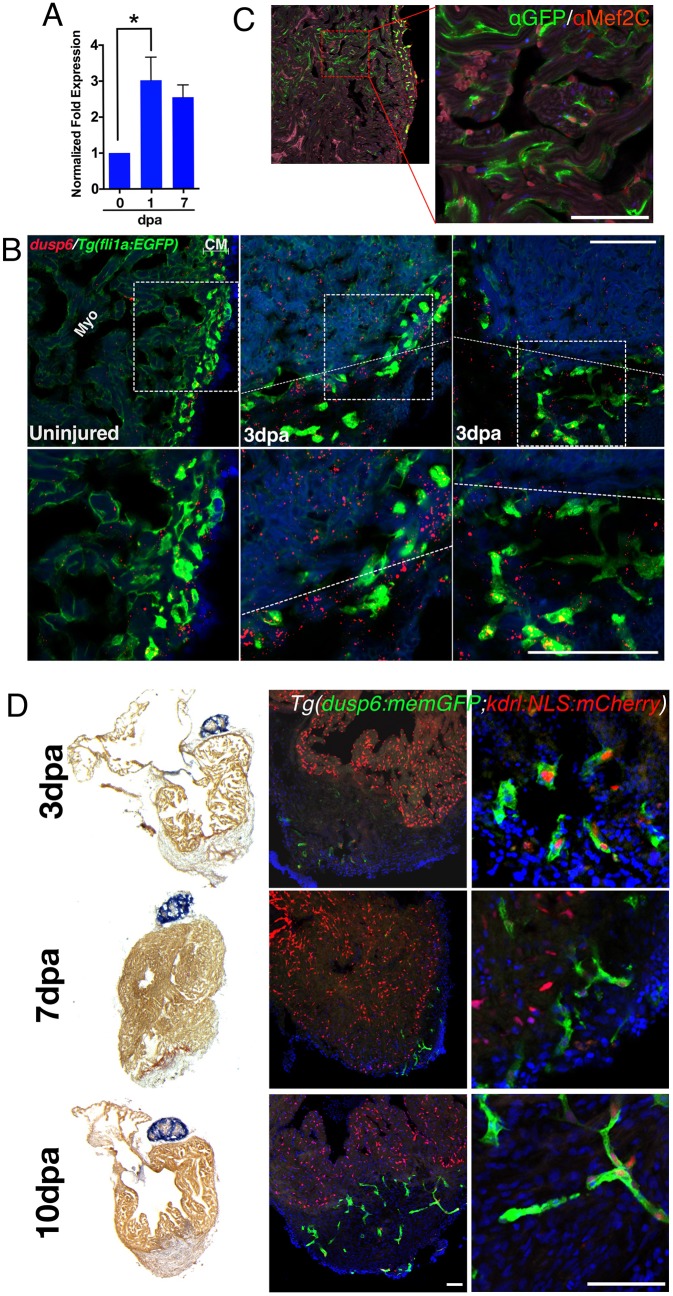
dusp6 is induced upon cardiac injury and expressed in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells. (A) Q-PCR analysis of dusp6 in adult zebrafish hearts at 1 and 7 days post amputation (dpa), compared with uninjured hearts. dusp6 is induced after ventricle apex amputation. Values are normalized to β-actin and rnap expression. Data represent three independent replicates. *P<0.05, one-way ANOVA. (B) dusp6 expression in uninjured hearts and at 3 dpa using RNAscope. In uninjured hearts, dusp6 (red) is weakly detected throughout the heart including endothelial cells [Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1], myocardium (Myo) and compact myocardium (CM). At 3 dpa, dusp6 expression was detected in the myocardium and in endothelial cells. Dotted line demarcates the amputation plane. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue) to visualize nuclei. Boxed areas are magnified beneath. (C) Confocal image from Tg(dusp6:memGFP)pt21 heart immunostained with anti-GFP and anti-Mef2C, showing that cardiomyocytes express memGFP in uninjured hearts. (D) AFOG images (left) and confocal images (center and right) of Tg(dusp6:memGFP)pt21; Tg(kdrl:NLS:mCherry)is5 hearts at multiple time points after ventricle apex amputation (n=3 for each time point). memGFP is expressed in the vessels of the compact myocardium in uninjured hearts and in the nascent vessels inside the clot after injury. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue) to visualize nuclei. Scale bars: 100 µm.