Fig. 2.
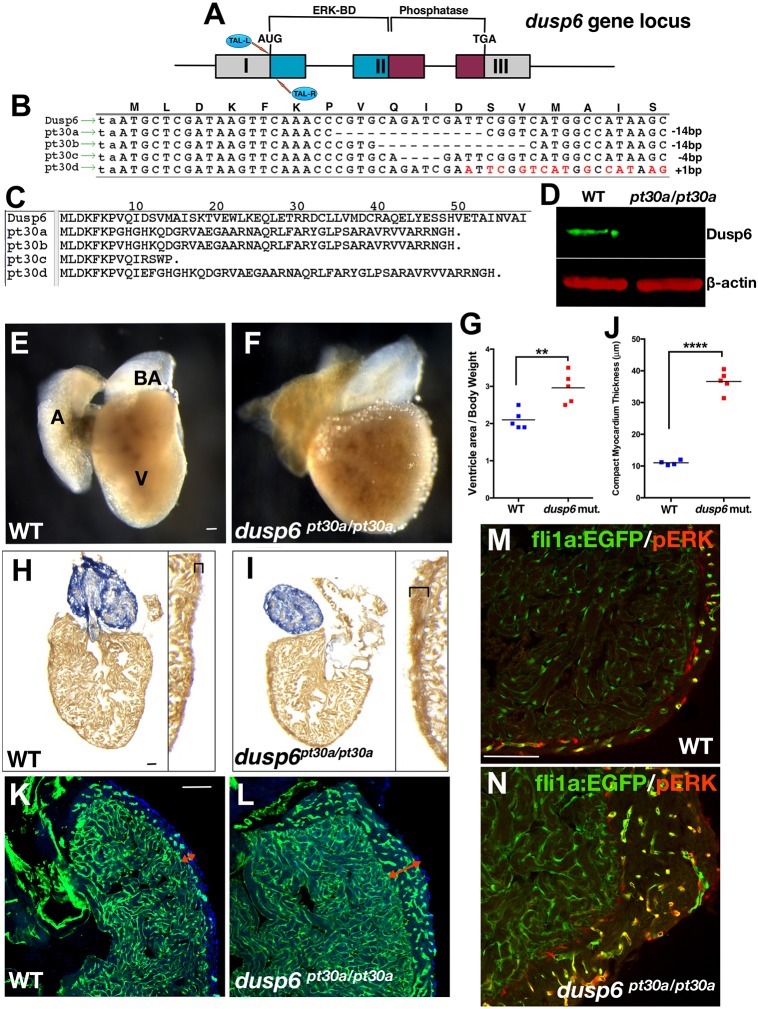
dusp6 mutant hearts exhibit mild cardiomegaly. (A) The TALENs targeting dusp6 exon 1. (B) Recovery of dusp6 mutant alleles pt30a-d. Mismatches created by the 1 bp insertion in pt30d are indicated in red. (C) Predicted amino acid sequence of dusp6pt30 alleles. (D) Western blot showing absence of Dusp6 protein in dusp6pt30a/pt30a embryos. β-actin was used as a loading control. (E,F) Whole-mount images of uninjured WT (E) and dusp6pt30a/pt30a (F) hearts at 5 months of age. dusp6 mutant hearts show cardiomegaly. A, atrium; V, ventricle; BA, bulbus arteriosus. (G) Quantification of the ratio of ventricle area/body weight (VA/BW) in WT (n=5) and dusp6 mutant (n=5) fish. dusp6pt30a/pt30a fish have a larger VA/BW ratio than WT fish. **P<0.01, Student's t-test. (H,I) AFOG staining of uninjured heart sections at 5 months of age. dusp6 mutant hearts (I) have a thicker compact myocardium (brackets) than WT hearts (H). (J) Quantification of compact myocardium thickness in uninjured hearts at 5 months of age for WT (n=4) and dusp6 mutant (n=5). ****P<0.0001, Student's t-test. (K,L) Sections of uninjured WT (n=4) and dusp6 mutant (n=4) fish with the Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 background to visualize the endothelium. dusp6 mutant hearts (L) have a thicker compact myocardium (red arrows) containing more vessels than WT hearts (K). (M,N) pERK is detected in fli1a:EGFP+ vessels of the compact myocardium. dusp6 mutant hearts (n=4) (N) have a thicker compact myocardium with more vessels showing pERK staining than in WT uninjured hearts (n=4) (M). Scale bars: 100 µm.