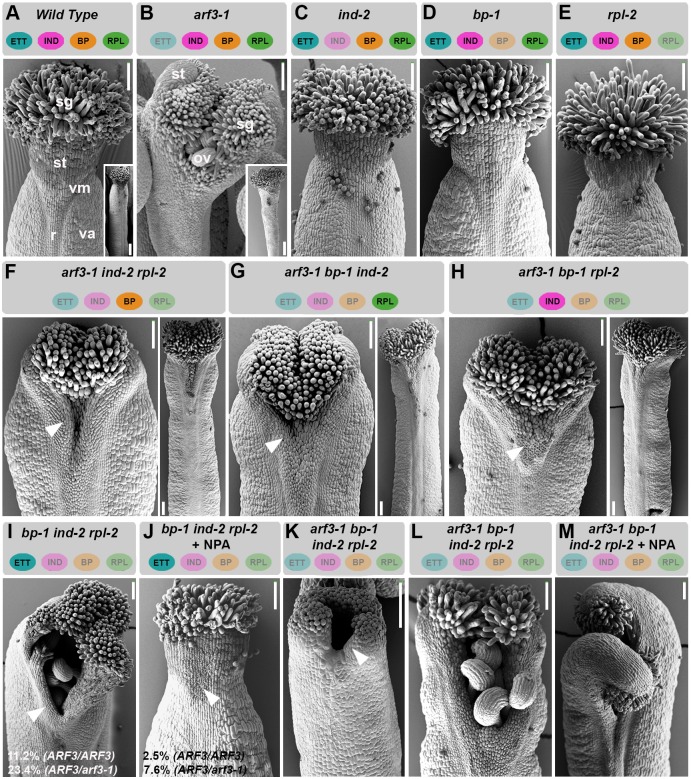
Fig. 2.
ETT, BP, RPL and IND genetically interact to ensure correct style formation. (A-E) SEM images of gynoecium apices and whole carpel (insets) of wild type (A), and arf3-1 (B), ind-2 (C), bp-1 (D) and rpl-2 (E) single mutants. Gynoecium apices and whole carpel images correspond to two different gynoecia of the same genotype. (F-H) SEM images of gynoecium apices of arf3-1 ind-2 rpl-2 (F), arf3-1 bp-1 ind-2 (G) and arf3-1 bp-1 rpl-2 (H) triple mutants and whole carpel (right). Gynoecium apices and whole carpel images correspond to two different gynoecia of the same genotype. Arrowheads point to regions of collapsed tissue at the gynoecium top. (I-J) SEM images of gynoecium apices of ind-2 bp-1 rpl-2 triple mutant without (I) and with (J) NPA treatment. (K-M) SEM image of gynoecium apex of arf3-1 ind-2 bp-1 rpl-2 quadruple mutant at stage 10 (K), at stage 12 (L) and at stage 12 after NPA treatment. Scale bars: 100 µm, 500 µm in insets. ov, ovules; r, replum; sg, stigma; st, style; va, valves; vm, valve margin.