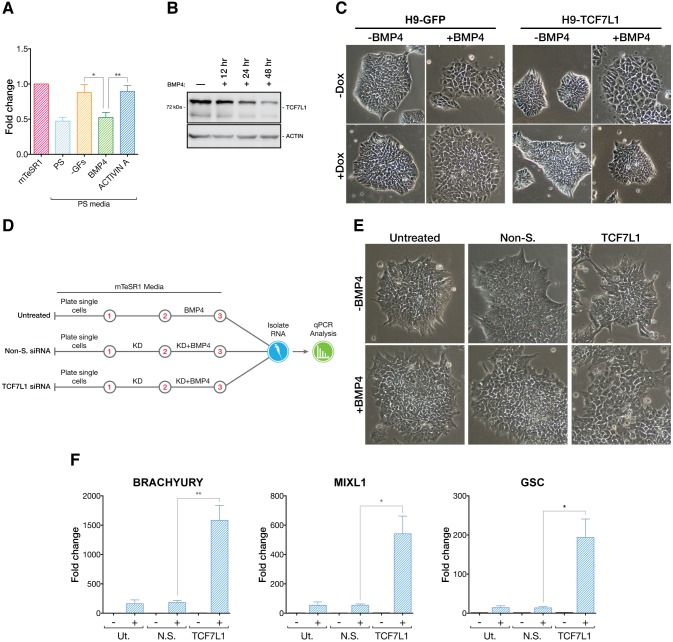
Fig. 6.
TCF7L1 antagonizes BMP4-induced differentiation. (A) qPCR analysis (n=3) of TCF7L1 mRNA levels after 24 h in mTeSR1, complete PS differentiation medium, PS differentiation medium without BMP4 and activin A (−GFs), or PS differentiation medium with either BMP4 or activin A alone. Two-tailed t-test, *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01. (B) Western blot analysis of TCF7L1 levels at 12, 24 and 48 h of BMP4-induced differentiation. (C) H9-GFP and H9-TCF7L1 cells were grown under feeder-free conditions and treated with BMP4 (24 h) while inducing GFP or TCF7L1 with doxycycline (1 μg/ml). Phase contrast images, original magnification 10×. (D) Scheme of experiment in which hESCs were treated with BMP4 (10 ng/ml) while performing TCF7L1 siRNA (50 nM) knockdown under feeder-free conditions. Cells were harvested after 48 h of siRNA knockdown and 24 h of BMP4 treatment. Control experiments were performed without BMP4 treatment for each condition (not shown). Red numbers indicate days of procedure. (E) Simultaneous loss of TCF7L1 and treatment with BMP4 causes pronounced morphological changes in colonies. Phase contrast images (original magnification 10×) show TCF7L1 siRNA+BMP4-treated hESC colonies, which appear more flattened and differentiated than controls. (F) qPCR analysis showing synergistic upregulation of PS markers when BMP4 treatment is combined with TCF7L1 knockdown (n=3). Two-tailed t-test, *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01. Error bars indicate s.e.m.