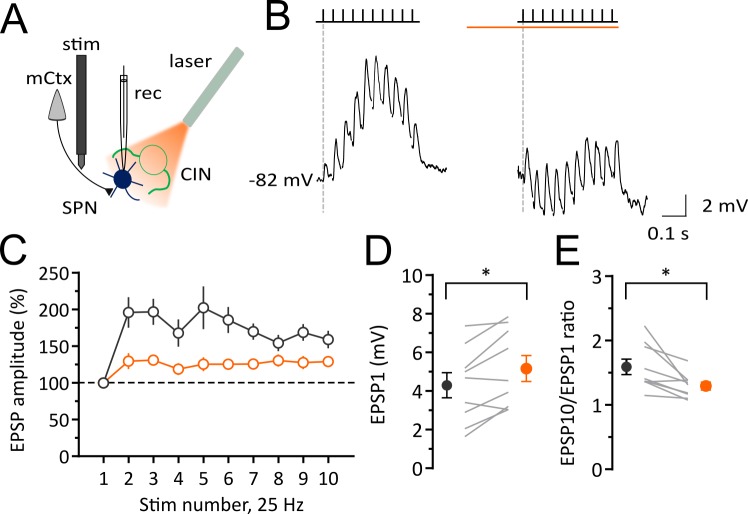
Figure 3. Light-induced pause in CINs decreases corticostriatal plasticity of SPNs in vivo.
Experimental configuration for whole-cell recordings of evoked EPSPs in SPNs during light-induced pauses of CINs. (B) Average trace of whole-cell current-clamp recording of EPSPs elicited by cortical stimulation (10 stimuli, 25 Hz) before (left) and during a pause (right). (C) Pooled data showing that facilitation is attenuated during a pause. (D) The first EPSP amplitude is significantly increased during a pause. (E) The ratio of last and first EPSPs is significantly decreased during a pause. Lines indicate individual cells and filled circles with error bars represent mean ± SEM. (N/n = 9/9) *p<0.05 with paired t-test. N = mice; n = cells.