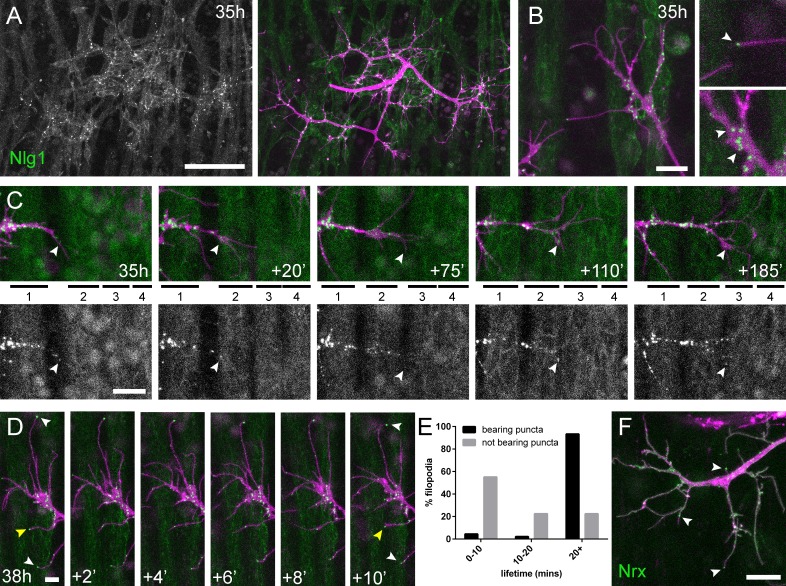
Figure 6. Neuritic Adhesion Complexes (NACs) containing Neurexin and Neuroligin 1 stabilise filopodia during arbor growth.
(A) Nlg1::GFP (Mef2-GAL4; green) expressed in muscles at 35 hr APF forms puncta on the postsynaptic membrane that are arranged exclusively in apposition with the axon terminals (VGlut-LexA > myr::tdTomato; magenta). (B) Higher magnifications show the concentration of Nlg1::GFP puncta at sites of branch growth and at filopodia tips. (C) Rounds of filopodia extension and stabilisation are concomitant with the recruitment of Nlg1::GFP puncta (white arrowheads) to their tips. Time series shows the extension of a branch across a muscle field at 35 hr APF (myotubes numbered from anterior to posterior). (D) Detail of relationship between the dynamics of filopodia and Nlg1::GFP puncta. Puncta (white arrowheads) mark the tips of filopodia that persist. Yellow arrowhead indicates a punctum marking the limit of filopodial retraction. (E) Relationship between lifetimes of filopodia and Nlg1::GFP puncta. Histogram showing lifetimes of filopodia with Nlg1::GFP puncta at their tips (n = 45) and without puncta at their tips (n = 49). Filopodia bearing Nlg1::GFP puncta were significantly longer lived than those without puncta (with puncta: 19.36 ± 2.82 mins, without puncta: 10.73 ± 6.88 mins, Mann-Whitney U = 305.5, p<0.0001, two-tailed). (F) Localisation of Nrx::GFP (OK371-GAL4; green) in PM-Mn growing axonal arborisation at 35 hr APF (mCD8::ChRFP; magenta). Arrowheads indicate puncta positioned on filopodia. Bars represent SDs. Scale bars: 50 µm (A), 10 µm (B,F), 20 µm (C), 5 µm (D).