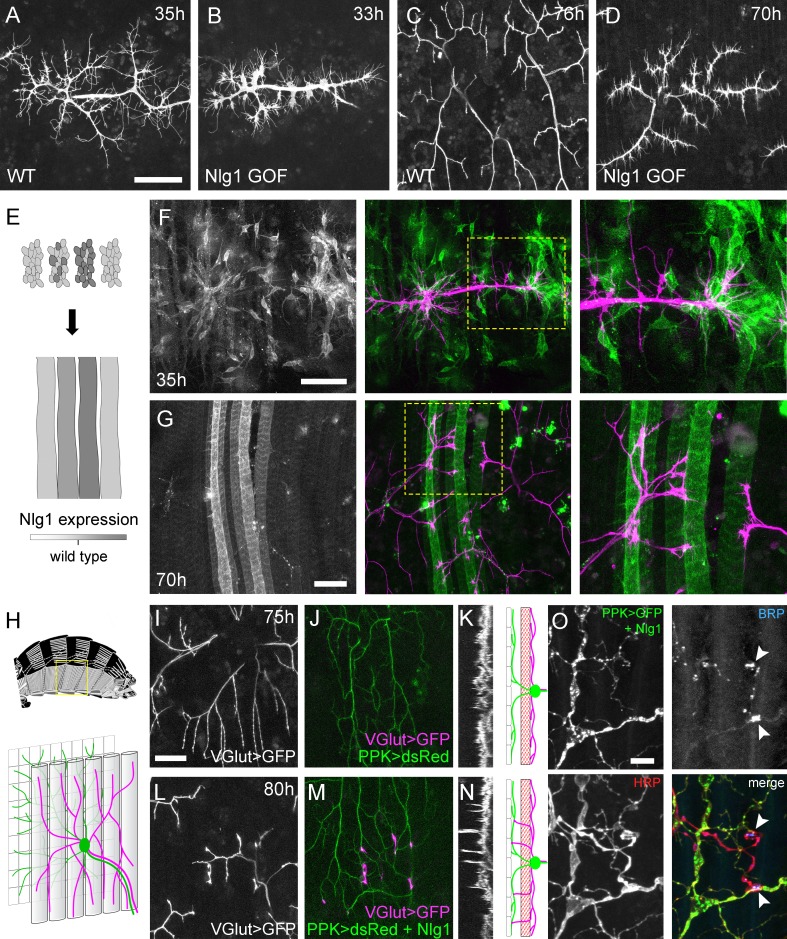
Figure 8. Neuroligin 1 acts locally to drive early arbor growth.
(A–D) Postsynaptic Nlg1 overexpression disrupts PM-Mn axon arbor growth. (A) Control PM-Mn arborisations at 35 hr APF and (B), PM-MN Arborisations at 33 hr APF in a background of postsynaptic Nlg1untagged expression (Mef2-GAL4; VGlut-LexA > myr::GFP). (C) Control arborisations at 76 hr APF. (D) arborisations in a background of muscle specific Nlg1untagged expression at 70 hr APF (E) Schematic of ‘flip-out’ clones generation. Muscle precursor clones induced with hsFlp at larval L3 stages produce clusters of GAL80 negative myoblasts which fuse to form ‘stripes’ of clonal muscle fibres expressing Nlg1untagged and myr::tdTomato. (F) At 35 hr APF, PM-Mn motoneuron branches (magenta) show preferential elaboration onto clonal Nlg1untagged expressing myotubes and myoblast clusters (green). (G) Axonal branches in contact with clonal, Nlg1untagged expressing muscle fibres show a hyper-stabilisation phenotype. Growth of branches appears to be preferentially directed along clonal fibres. (H–O) Ectopic expression of Nlg1 in class IV da sensory neurons drives changes in motoneuron axonal arbor morphology. (H) Schematic shows the relative positions of class IV v’ada sensory input arborisations (green), pleural muscles (grey tubes) and motor axon arborisations (magenta) in the pleural abdominal body wall (schematic of musculature adapted from Demerec, 1950). (I) Motoneuron axon terminals expressing myr::GFP (VGlut-LexA) at 80 hr APF in a control (J) the v’ada input arborisations in the same region expressing dsRed (PPK-Gal4; Grueber et al., 2003). (K) Transverse projection shows the PM-Mn axon arborisations restricted to a single plane. Schematic transverse shows the separation of the v’ada arborisation (green) from the motor axon terminals (magenta) by the pleural muscles (red). (L–N) Nlg1untagged expression in class IV da sensory neurons results in axonal branches that penetrate gaps between the muscle fibres and make contact with the sensory arborisations. These aberrant branches are shown in the transverse view and run perpendicularly to the rest of the arborisation. (O) Abdominal fillet of a newly eclosed adult expressing Nlg1untagged and CD8::GFP in the class IV da sensory neurons. Anti-HRP reveals the motor axon terminals and BRP immunoreactivity reveals presynaptic specialisations at contacts between motor axons and the sensory arborisation (arrowheads). Scale bars: 50 µm (A,B,C,D,F,G), 25 µm (I,J,L,M), 5 µm (O).