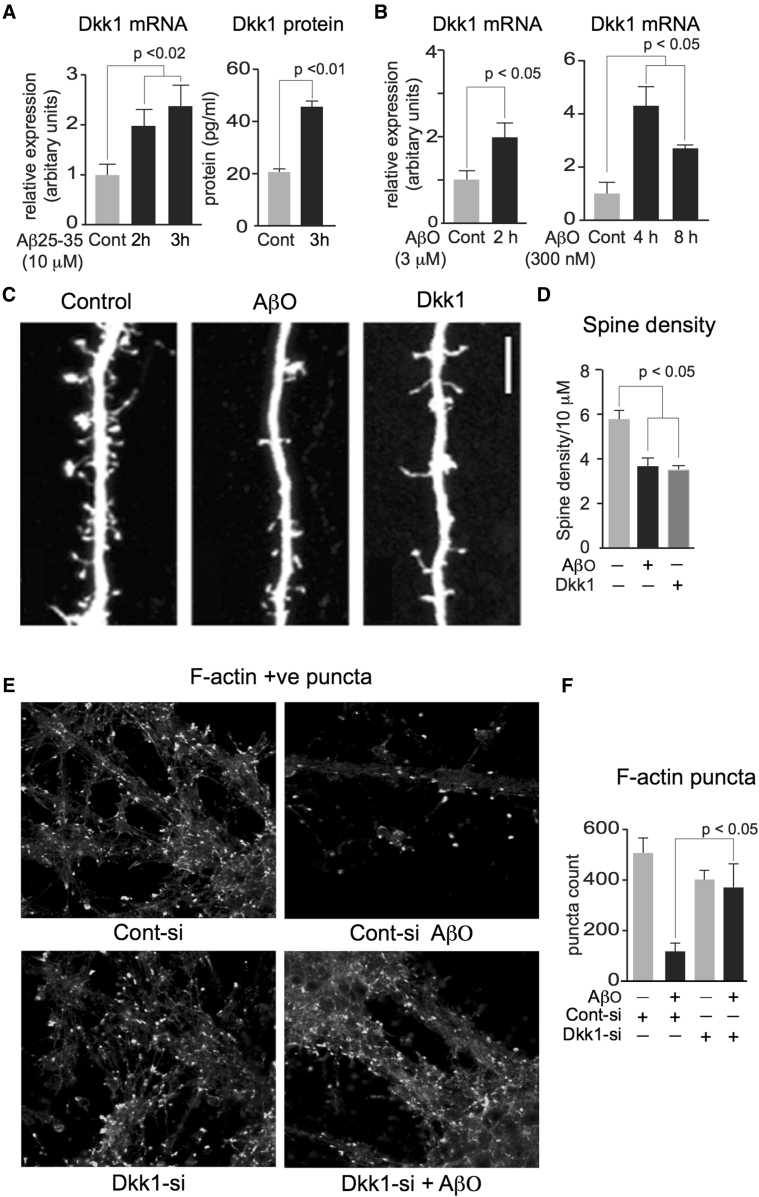
Fig. 1.
Aβ synaptotoxicity is Dkk1 dependent. (A) Rat primary cortical neuronal cultures (14 d.i.v.) were treated with 10 μM Aβ25–35 for 2 and 3 hours, cells were harvested for RNA extraction, and media were collected for protein analysis. cDNA was generated and qRT-PCR performed to determine rat Dkk1 mRNA levels, left. Secreted Dkk1 protein levels in media were measured by ELISA, right. (B) Similar cultures were treated at 3 μM and 300 nM with AβO preparation for the times indicated and harvested, and Dkk1 mRNA levels were determined as mentioned previously. (C and D) Similar cultures were transfected with eGFP at 24 d.i.v., 48 hours later treated for 4 hours with 2 μM AβO, or for 3 hours with 400 ng/mL Dkk1, fixed, imaged by confocal microscopy, and dendritic spine density and morphology assessed. Both treatments resulted in a significant reduction in dendritic spine linear density, quantified in (D), scale bar = 5 μM. Dendritic spine linear density/10 μm: control, 5.8 ± 0.41; AβO, 3.7 ± 0.34; Dkk1, 3.5 ± 0.31; P < .001 for all treatments. (E and F) Similar cultures were treated overnight with Dkk1-siRNA duplex, or a scrambled version as control, each linked to the Pen-1 peptide. Next day, cells were treated with 2 μM AβO for 4 hours, fixed, and fluorescently labeled with phalloidin-488, imaged (E), and F-actin–labeled puncta quantified (F), scale bar = 50 μM. In all the aforementioned, significance was determined by ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc t-test. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Abbreviations: AβO, amyloid β (1–42) oligomers; ANOVA, analysis of variance; d.i.v., days in vitro; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; Dkk1, Dickkopf-1.