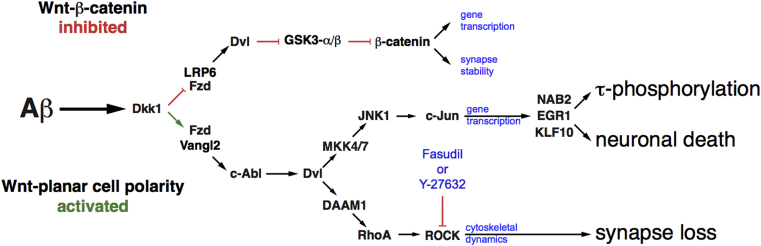
Fig. 5.
Schematic of Aβ-driven Wnt-PCP pathway activation. Aβ drives a rapid increase in Dkk1 expression. Concomitant with antagonism of canonical Wnt-β-catenin–signaling Dkk1 then drives the activation of the Wnt-PCP pathway by antagonizing the LRP6-Fzd interaction. We have previously shown that activity in the JNK/c-Jun arm of Wnt-PCP induces the expression of several identified genes required for Aβ-driven increases in tau phosphorylation and neuronal death to occur. Here, we demonstrate that activity of the Daam1/RhoA/ROCK arm is necessary for Aβ-driven synaptotoxicity and that this can be blocked by ROCK inhibitors Y-27632 or fasudil. Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid β; c-Abl1, c-Abl oncogene 1, nonreceptor tyrosine kinase (ABL1); DAAM1, disheveled associated activator of morphogenesis 1; Dkk1, Dickkopf-1; Dvl, disheveled; EGR1, early growth response 1; Fzd, frizzled; GSK3-α/β, glycogen synthase kinase-α/β; JNK1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (MAPK8); KLF10, Krüppel-like factor 10; LRP6, low-density lipoprotein receptor–related protein 6; MKK4/7, mitogen-activated protein kinase 4/7 (MAP2K4 and MAP2K7); NAB2, NGFI-A binding protein 2; PCP, planar cell polarity; RhoA, Ras homolog family member A; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase; Vangl2, Van Gogh–like protein 2.