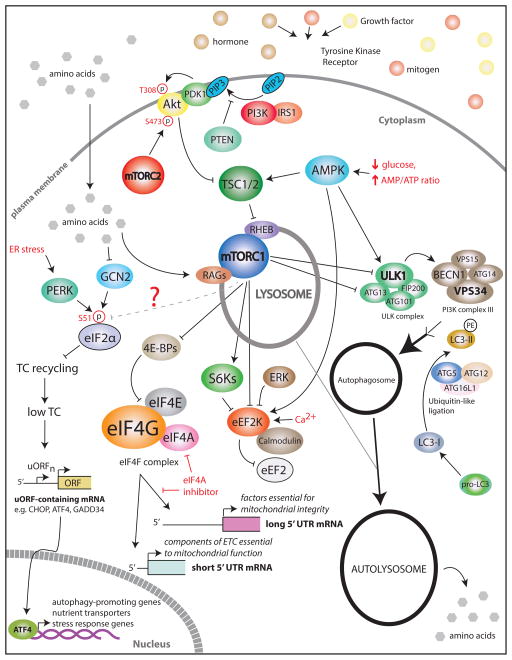
Figure 1. Schematic presentation of the orchestration of protein synthesis, energy metabolism and autophagy.
mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2) are two functionally and structurally distinct complexes. In response to growth factors (e.g. IGFs) and hormones (e.g. insulin), mTORC1 is activated via the PI3K/AKT/TSC/RHEB pathway, whereas amino acids activate mTORC1 via RAG GTPases (reviewed in [4]). mTORC1 phosphorylates and inactivates translational inhibitor 4E-BPs, which then allows eIF4F complex assembly. Increased levels of eIF4F lead to reprogramming of the translatome which in part leads to selective increase in translation of long 5′UTR mRNAs that encode factors that protect mitochondrial integrity, and short 5′UTR mRNAs which encode components of the electron transport chain (ETC) complex. When energy resources are limiting, AMPK is activated to reduce anabolic processes, while stimulating catabolic ones (reviewed in [5]. This is in part achieved by inhibition of mTORC1. eEF2K phosphorylates eEF2 which interferes with its ribosomal association and reduces elongation rates. This suppresses protein synthesis and reduces energy consumption. mTORC1 and ERK inactivate eEF2K thereby increasing protein synthesis, whereas AMPK activates eEF2K and reduces translation rates. GCN2 and PERK are major eIF2α kinases that sense nutritional (e.g. limited glucose, amino acids etc.) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, respectively. eIF2α phosphorylation coincides with reduction in ternary complex (TC) levels. This leads to the suppression of global translation while translationally activating some of the upstream open reading frame (uORF) containing mRNAs including CHOP, ATF4, GADD34. ATF4 induces upregulation of amino acid transporters and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases as well as a number of autophagy protein-encoding genes, including p62, ATG16L, LC3B, ATG12, ATG3, and BECN1. AMPK is a major positive regulator of the autophagy protein ULK1, while mTORC1 is a major negative regulator of autophagy. The ULK1 complex functions to initiate autophagosome formation along with the PI3K complex. This increased autophagic flux allows for cytoplasmic components to be recycled during acute nutrient starvation to feed back into the synthesis of vital proteins. Collectively, mTOR, AMPK, and eIF2α kinases coordination show multifaceted signaling nodes of nutrient sensing, translation, and autophagy. Of note, this representation of the pathways is simplified to highlight the mechanisms of coordination of mRNA translation, metabolism and autophagy. Detailed representation of mTOR, AMPK pathways and autophagy can be found in [4,5,64].