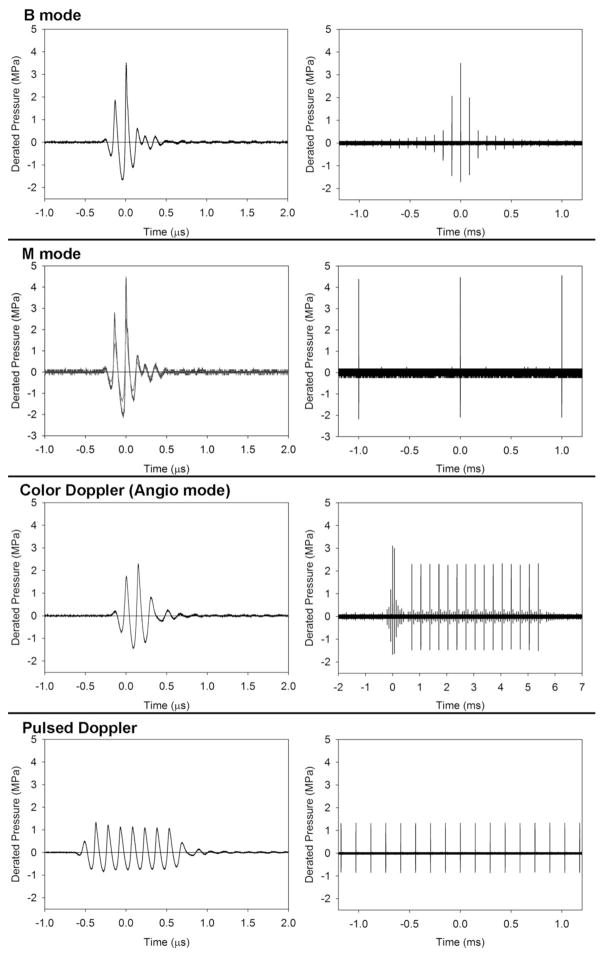
Figure 1.
A display of the pulse waveforms for each of the diagnostic ultrasound modes used. The power levels were the lowest settings with statistically significant pulmonary capillary hemorrhage. For B and Angio Doppler imaging modes, the pulses are short (left column) and several pulses appear in the sequence as the scanning beam passes by the hydrophone (right column). For B mode, this produces a rapid rise and fall of amplitudes. For the Angio Doppler mode, there is a brief B-mode sequence, for the greyscale background image, and sequences of 15 pulses which accurately determine the motion (normally blood flow). This sequence also passes by the hydrophone with rising and falling amplitudes; here only the maximum sequence is shown at the center of the Doppler box. For the fixed beam pulsed modes, the sequence (right column) is simply a pulse train at the pulse repetition period. The M mode pulse (left column) is the same for both the 15 s and 5 min exposures. The pulsed-Doppler pulse is relatively long to yield accurate velocity measurements within the sample volume.