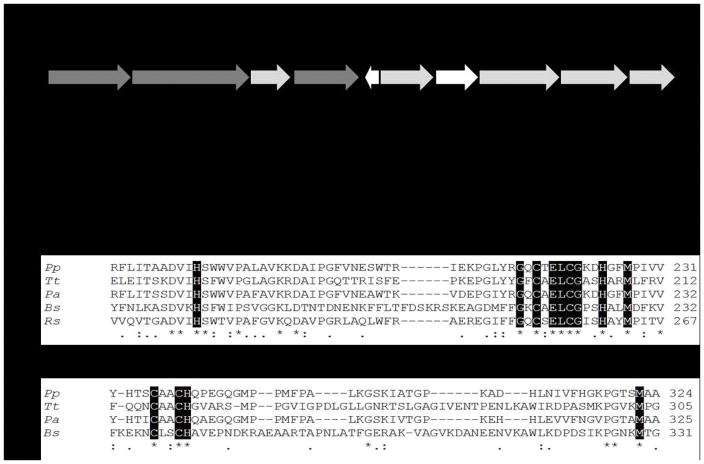
Figure 1.
A. Organization of the Caa3-Cox gene cluster in KF707: dark gray, functional genes (coxIIc-I-III); light gray, genes for Caa3-Cox biogenesis and white, genes probably not directly related to Caa3-Cox. B. Alignment analysis for subunit II of the caa3-type Cox from KF707 (Pp - BAU71737), T. thermophilus (Tt – AFH37994), P. aeruginosa (Pa – ONM68414) and B. subtilis (Bs – OBA08775), and aa3-type Cox from R. sphaeroides (Rs – ASN35548). The first alignment focuses on the cupredoxin domain and the copper center CuA (N-terminal portion), and the second one shows the cytochrome c domain (C-terminal portion), absent in the aa3-type Cox from R. sphaeroides. The dark boxes are the amino acids that are directly involved in the CuA and haem c binding, asterisks and dots represent the fully and partially conserved amino acid residues, respectively. Analyses were performed using the ClustalW software [20].