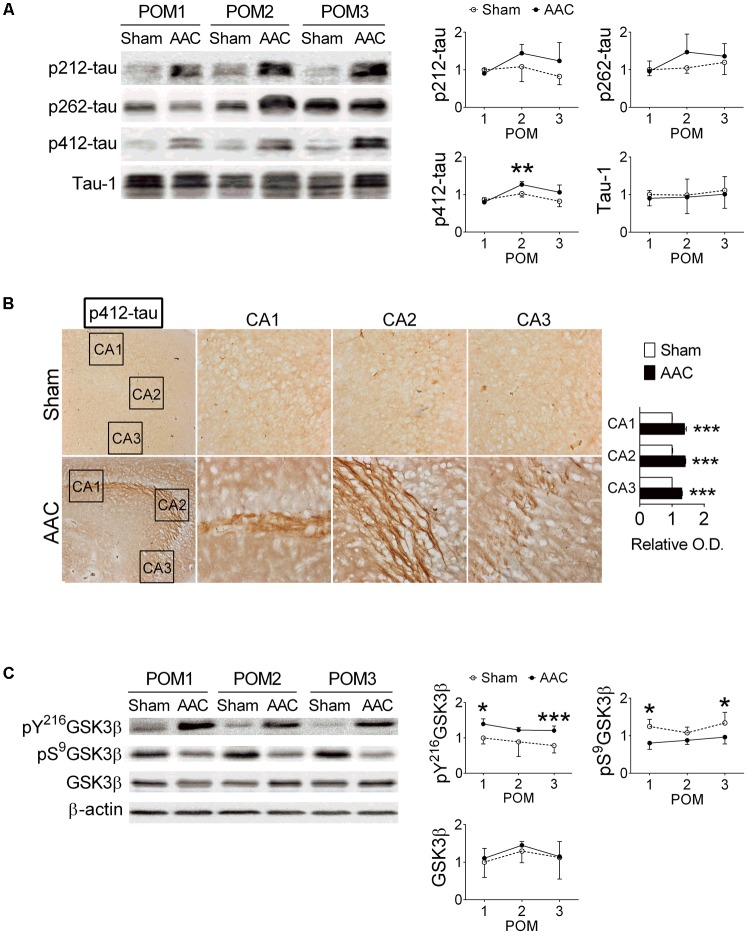
FIGURE 3.
Abdominal aortic constriction increased levels of phosphorylated tau protein in the hippocampi of pigs. 7-month-old pigs were given the AAC or the Sham operation, and their hippocampi at POMs 1, 2, and 3 were removed for analyses. (A) Relative levels of p212-, p262-, p412-, and total tau (Tau-1). Representative immunoblotting micrographs are shown on the left panels; the quantitative results are shown on the right panels. N = POM 1: Sham: 3, AAC: 4; POM 2: Sham: 3, AAC: 5; POM 3: Sham: 6, AAC: 7. (B) Expression of p412-tau in the hippocampi of POM 3 pigs. Representative immunostaining micrographs are shown on the left panels; the quantitative results of relative optical density (O.D.) are shown on the right panel. N = Sham: 3, AAC: 3. (C) Relative levels of pY216GSK3β, pS9GSK3β, GSK3β, and β-actin. Representative immunoblotting micrographs are shown on the left panels; the quantitative results are shown on the right panels. N = POM 1: Sham: 3, AAC: 4; POM 2: Sham: 3, AAC: 5; POM 3: Sham: 6, AAC: 7. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus respective Sham group, Bonferroni’s post hoc test. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure S3.