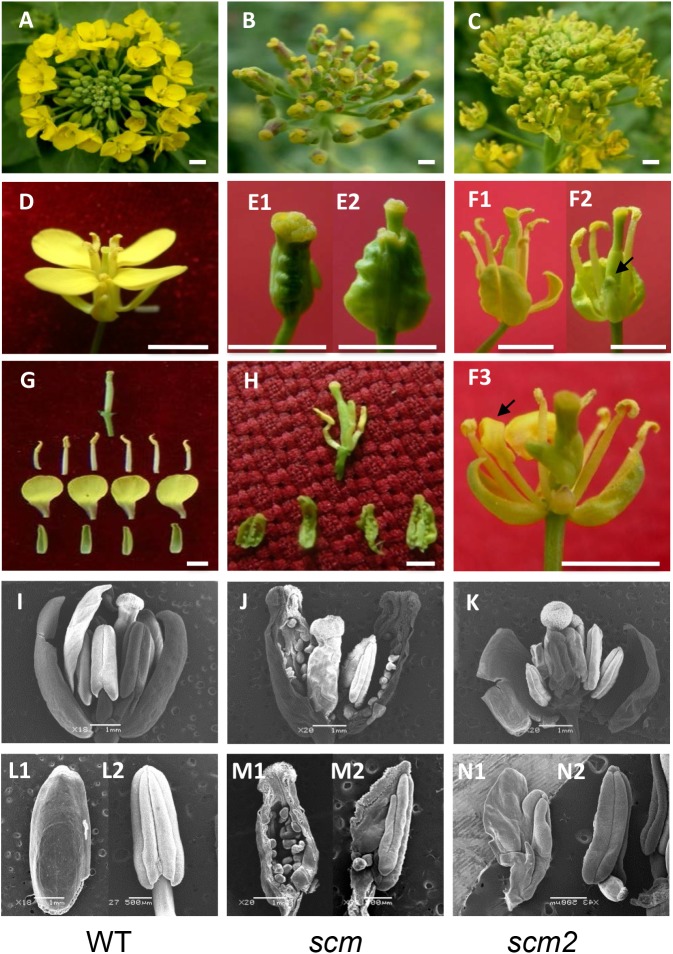
FIGURE 1.
Characteristics the sepal carpeloid mutants of Brassica. (A–C): inflorescence; (D,E1,E2,F1–F3): flower; (G,H): floral organs; (I–K): SEM photos of flowers; (L1,L2,M1,M2,N1,N2): SEM photos of floral organs; (A,D,G,I,L1,L2): wild type Brassica (WT). (L1,L2) Are sepal (left) and stamen (right); (B,E1,E2,H,J,M1,M2): the typical sepal carpeloid mutant (scm). M1 is a sepal carpeloid organ, and M2 is an incomplete stamen to carpel organ with one ovule; (C,F1–F3,K,N1,N2): the incomplete sepal carpeloid mutant (scm2). Arrows indicate sepal carpel-like transition in F2 and petal stamen-like transition in F3. N1 is an incomplete petal to stamen organ, and N2 is a stamen of scm2. Bars in E1 and E2 are 5 mm; bars in I–K,L1,M1 are 1 mm; bars in L2,M2,N1,N2 are 500 μm; and bars in the others are 10 mm.