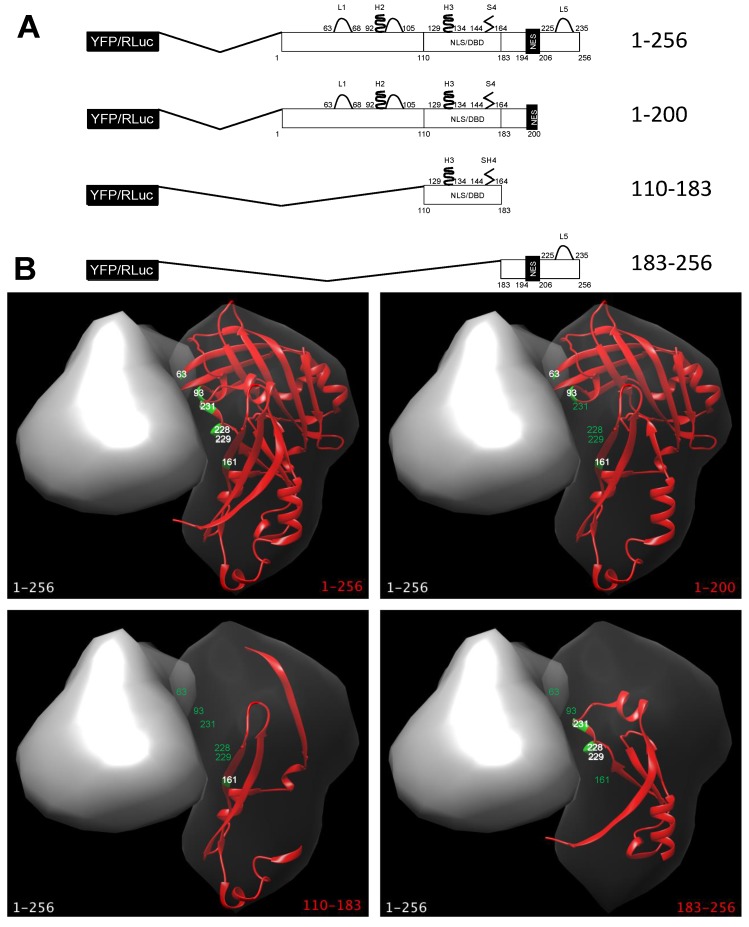
Figure 1.
M deletion mutants used in this study (A) Schematic representation of R espiratory syncytial virus (RSV) matrix (M) deletion mutants used in this study as fused to either YFP, RLuc and cyan fluorescent protein (CFP). Elements involved in dimerization are shown, based on the nomenclature used in [26]. L1, loop 1 (aas 63–88); H2, helix 2 and downstream loop (aas 92–105); H3, helix 3 (aas 129–134); S4, sheet 4 (aas 144–163); L5, loop 5 (225–235); NLS/DBD, nuclear localization sequence/DNA binding domain (residues 110–183); NES, nuclear export sequence (aas 194–206); YFP, yellow fluorescent protein; RLuc, Renilla luciferase; (B) The recently solved M dimeric structure (PDB code 4V23) was used to highlight the key aas involved in M dimerization and their position relative to each deletion mutant tested in this study, using software Chimera as described in the Materials and Methods section. The surface of a full-length M monomer (1–256) is shown as a grey structure in combination with the M versions used in this study, shown as red ribbons. Key residues involved in dimerization in the latter subunit are shown in green. Residue labels are shown either in white or green, depending on their presence or absence in the corresponding deletion mutant, respectively.