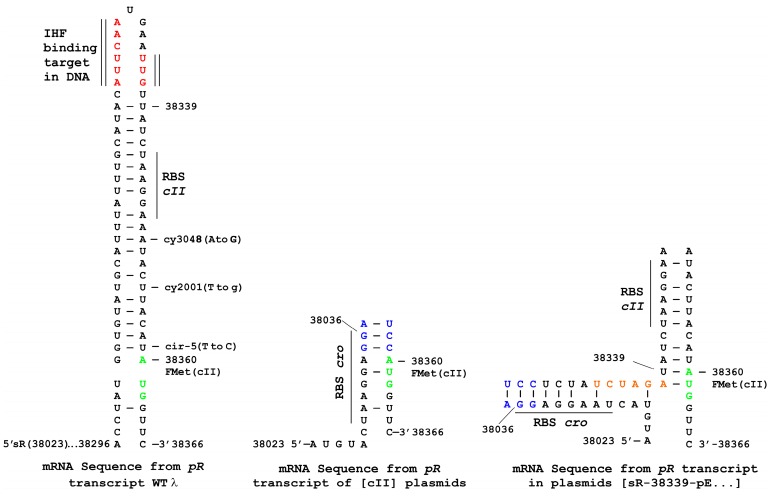
Figure 2.
Potential stem-loop configurations in pR mRNA ahead of cII drawn from λWT and synthetic cII expression plasmids. In each structure, the start site for pR-initiated mRNA is suggested as arising at λ sequence base 38,302 just downstream from pR [48]. The structure on left omits the cro-nutR-tR1 sequence and was inspired from a drawing in [36] showing the potential for stem loop mRNA secondary structure ahead of the translational start for cII that could impede translational initiation. The FMet codon for cII is green. An IHF (integration host factor) binding site in DNA [47] is shown in red which resembles the IHF consensus sequence AAAAAAnnnTTnnnWATCAAnnnTTR (where W is A or T, R is A or G and N is any nucleotide) but lacks the A-tract region about one helical turn from the consensus region [49]. The positions for some of the mutations [36] influencing cII that fall within the stem loop are shown. The structure in the middle includes the mRNA sequence produced from plasmid [CII]. This eliminates the stem-loop mRNA structure ahead of cII found in WT λ. It includes the WT λ sequence downstream from pR (bases 37,985–38,036 shown in Figure 1), the mRNA start site at 38,023 and the RBS for cro that is placed four bases ahead of the Fmet codon for cII (refer to Figure S1 and Materials and Methods). This arrangement included a base change equivalent to mutation cir-5 one base ahead of the FMet ATG starting at 38,360 of cII. The cir-5 mutation was suggested [36] to suppress the effect of mutation cII3086 at 38,360, which changes the ATG to GTG. The structure on the right includes plasmids that have the λ sequence for the 38,023 sR transcriptional start site downstream of pR and the WT λ DNA sequence downstream of base 38,339 (just downstream of the IHF binding site shown on figure at left), including the WT pE sequence. The bases for the BamHI (blue) and XbaI (pink) sites in middle and right drawings are shown as DNA sequences in Figure S1 (Plasmid groups 1 and 3, respectively).