Table 1. Suzuki–Miyaura coupling of various aryl halides using PdNP@3a and Pd(PPh3)4 a , b .
| Entry | Aryl halide | Product | Yield [%] |
|
| PdNP@3a | Pd(PPh3)4 | |||
| 1 |
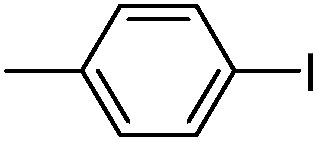
|
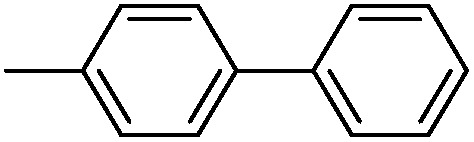
|
99 | 86, (99 c , 98 d , 22 e ) |
| 2 |
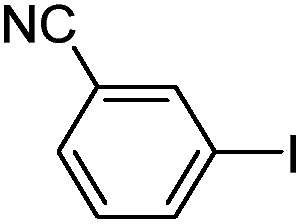
|
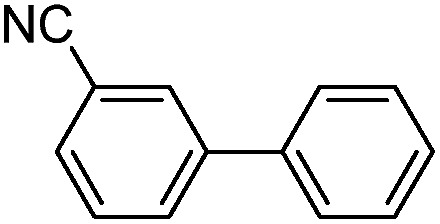
|
>99 | 81 |
| 3 |
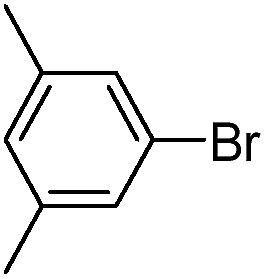
|
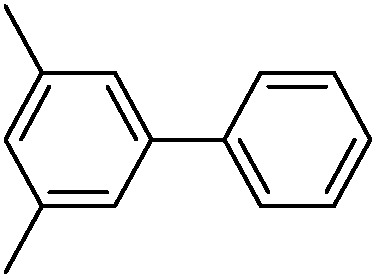
|
96 | 85 |
| 4 |
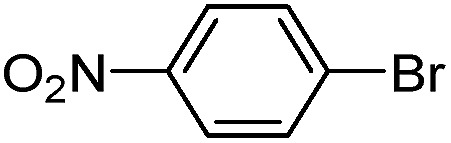
|
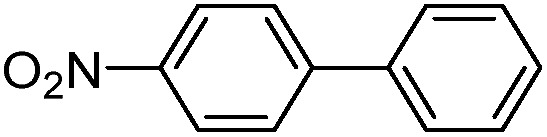
|
>99, >99 f | 78, 40 f |
| 5 |
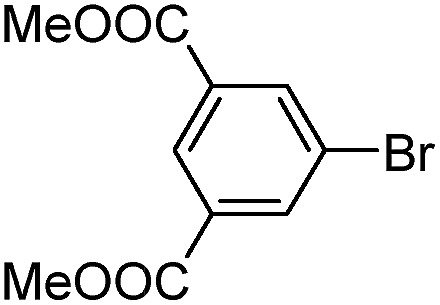
|
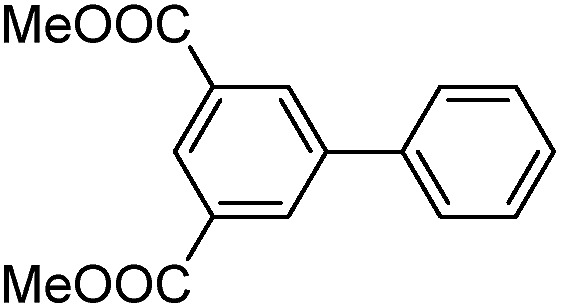
|
>99 | 73 |
| 6 g |
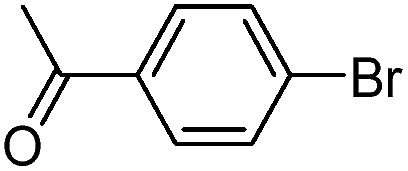
|
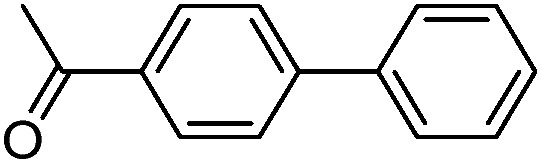
|
99 ± 0.4 | 75, (78 c , 72 d , 20 ± 2.4 e ) |
aReaction conditions: aryl halide (0.057 mmol), phenylboronic acid (0.087 mmol), Na2CO3 (0.17 mmol), Pd catalyst (0.57 μmol, 1.0 mol%).
bYields are based on 1H NMR analysis of the crude products.
cFor Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 catalyst.
dFor Pd2(dba)3.
eFor Pd/C (5%).
fAfter exposure of the catalyst to air for 2.5 h.
g5 repeats with a standard deviation for both PdNP@3a and Pd/C (5%).
