Table 1. Optimization of the catalytic reductive aminocarbonylation of aryl iodide with nitroarene.
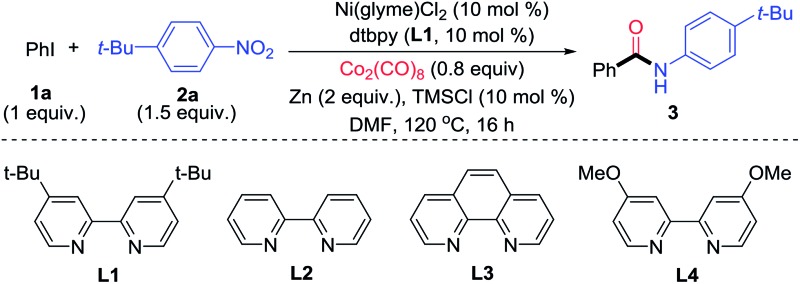
| ||
| Entry | Variations from ‘standard conditions’ | Yield a |
| 1 | None | 100 |
| 2 | L2 instead of L1 | 92 |
| 3 | L3 instead of L1 | 91 |
| 4 | L4 instead of L1 | 87 |
| 5 | Mn (2 equiv.) instead of Zn | 58 |
| 6 | NMP instead of DMF | 85 |
| 7 | Fe(CO)5 (2 equiv.) instead of Co2(CO)8 | 26 |
| 8 | Mo(CO)6 (2 equiv.) instead of Co2(CO)8 | 31 |
| 9 | CO (1.4–2.4 bar) instead of Co2(CO)8 | 6–16 |
| 10 | FeBr2 (10 mol%) instead of Ni(glyme)Cl2 | 10 |
| 11 | CoCl2 (10 mol%) instead of Ni(glyme)Cl2 | <5 |
| 12 | CuBr2 (10 mol%) instead of Ni(glyme)Cl2 | <5 |
| 13 | MnCl2 (10 mol%) instead of Ni(glyme)Cl2 | <5 |
| 14 | No Ni(glyme)Cl2 | <5 |
| 15 | No L1 | 55 |
aCorrected GC yield using n-dodecane as an internal standard.
