Fig. 5.
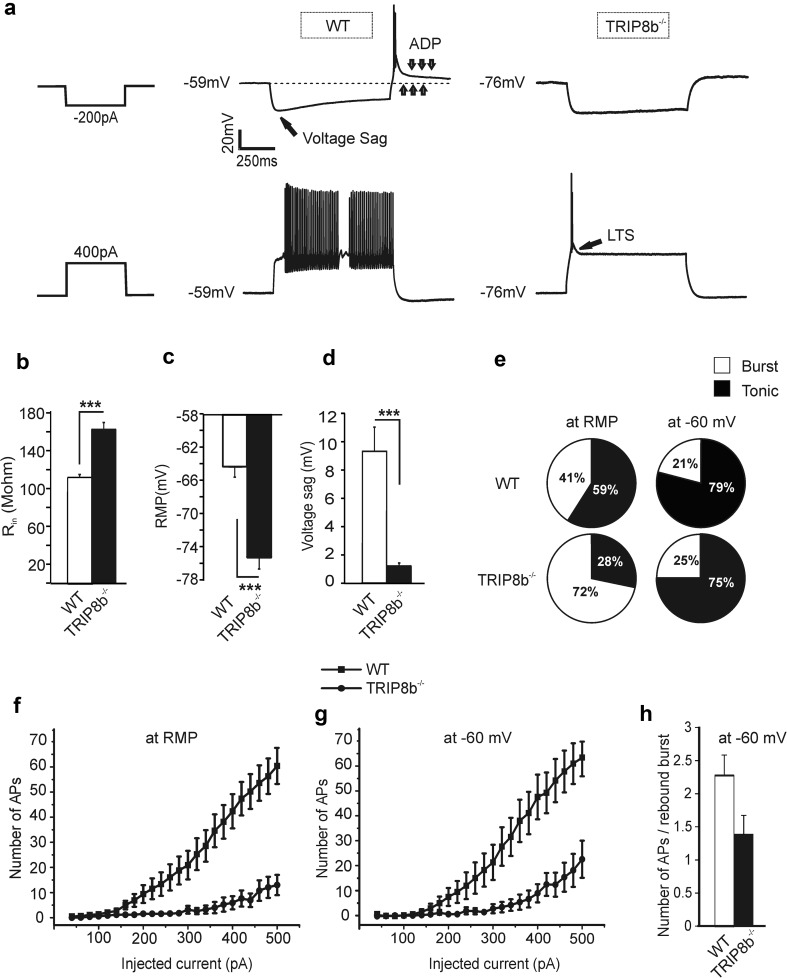
Changes in firing pattern and intrinsic properties of the TC neurons in TRIP8b−/− mice. a Sample traces recorded in response to the injection of hyperpolarizing and depolarizing currents from the RMP of TC neurons in the VB complex of WT and TRIP8b−/− mice. Note the different behavior of cells in response to the positive and negative current injections. LTS (see arrow, lower right panel) and ADP (3 downward arrows, upper panel) represent low-threshold Ca2+ spike and Ih-dependent afterdepolarizing potential, respectively. The 3 upward arrows indicate RMP. b and c show the higher Rin and significantly hyperpolarized RMP of TC neurons in TRIP8b−/− compared to WT mice (Student’s t tests. ** and *** indicate, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively). d Bar graph showing a significant reduction in the I h-dependent voltage sag in TRIP8b−/− (Student’s t tests, *** indicates p < 0.001).The voltage sag was measured upon injection of a hyperpolarizing current of -200 pA. e Pie charts indicating the percentage (%) of burst activity in TC neurons of TRIP8b−/− (72%, n = 14 cells) compared to WT mice (41%, n = 22 cells), when cells were challenged with depolarizing currents from RMP (left panels). The occurrence of burst firing was no longer different between the two groups when TC neurons were held at a more depolarized potential of around − 60 mV by DC current injection (right panels). f The number of APs elicited by the injection of positive currents with 20 pA increments from RMP is shown. Significantly (Repeated-measures ANOVA, p < 0.001) less APs were evoked in TRIP8b−/− TC neurons. g The number of depolarization-induced APs in TRIP8b−/− TC neurons after compensation of the membrane hyperpolarization by injection of a small positive DC current (holding the RMP at − 60 mV) was still significantly (repeated-measures ANOVA, p < 0.001) lower compared to the WT TC neurons. h Bar graph comparing the number of APs on rebound burst in WT and TRIP8b−/− VB TC neurons