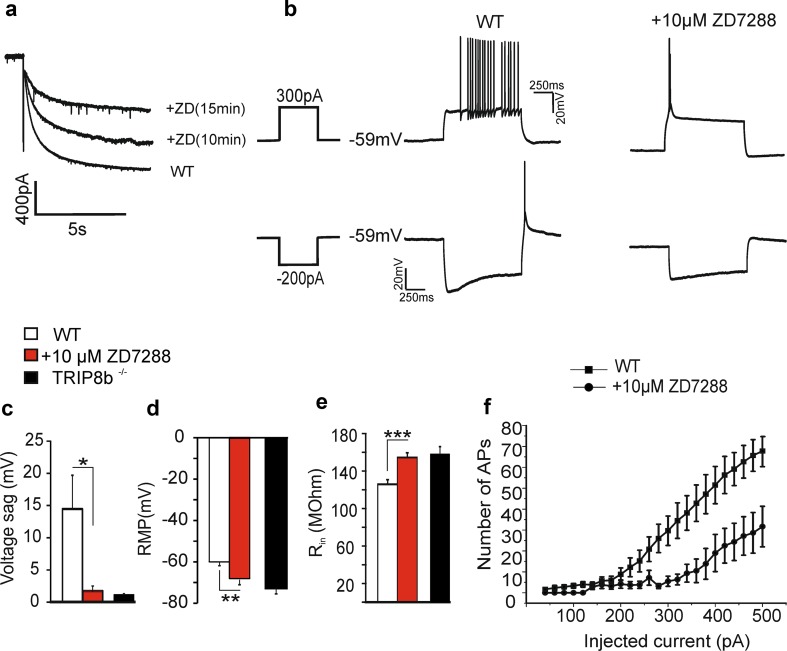
Fig. 6.
Reduction of I h in thalamic relay neurons by ZD7288. a Sample traces recorded under voltage-clamp conditions in the presence of 10 µM ZD7288 from TC neurons of the VB complex of WT mice. The reduction of I h after 15 min of blocker application resembles the I h amplitude in TRIP8b−/− mice (see Supplemental Figure 7). b Sample traces obtained from current-clamp recordings demonstrating the changes in firing pattern and RMP of TC neurons following application of 10 µM ZD7288. c Bar graph showing the significant reduction in the voltage sag upon current injection of − 200 pA (n = 6). The reduction in the voltage sag is comparable with the values obtained from TRIP8b−/− relay neurons. The reduction in I h density is accompanied by a significant (ANOVAs, p < 0.001) shift to hyperpolarizing potentials in RMP of WT TC neurons (d) and an increase in R in (e). As shown in (f) the number of APs elicited by the injection of positive currents with 20 pA increment from RMP after bath application of ZD7288 (filled circles) is significantly smaller (ANOVAs, p < 0.001) than under control conditions (filled squares)