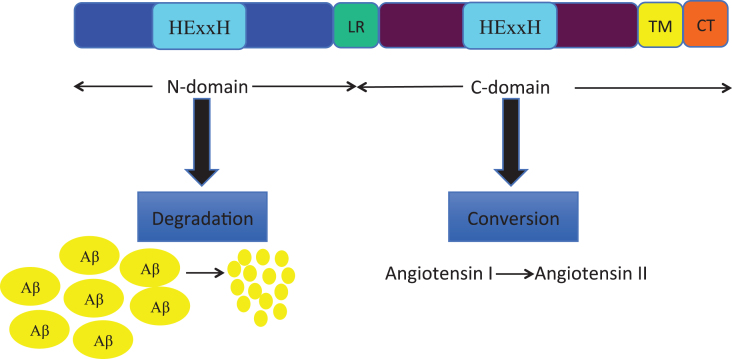
Fig.1.
Human ACE-1 structure and domains specificity. Schematic representation of human ACE-1 domains structure. The two homologous domains (N-domain and C-domain) have a catalytic active zinc binding site (HExxH). The N-domain and most of C-domain are extracellular. Both domains are linked by a linker sequence (LR), while a transmembrane (TM) domain joins the C-domain with an intracellular C-terminus (CT) (adapted from [89]). The figure illustrates how N- and C-domains of ACE-1 differentially perform the reported roles of Aβ cleavage (N-domain) and more widely recognized conversion by angiotensin converting activity of angiotensin I to angiotensin II (C-domain).