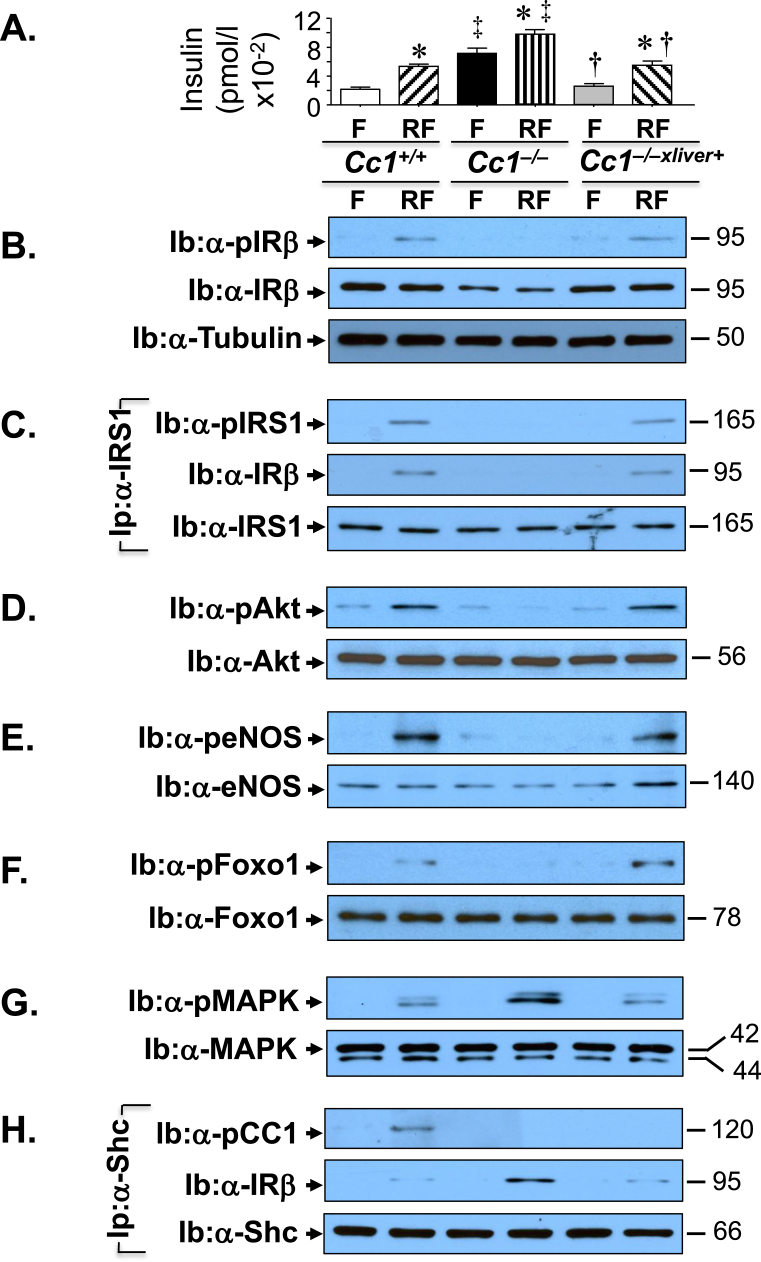
Figure 4.
Insulin signaling in aorta. (A) Mice (8 months of age, n = 6/genotype/treatment) were fasted (F) overnight and refed for 7 h (RF) before retro-orbital venous blood was drawn and plasma insulin levels were assayed, as indicated in the graph [Cc1+/+ (white for F and right diagonal stripes for RF), Cc1−/− (black for F and vertical stripes for RF), and Cc1−/−xliver+ (gray for F and left diagonal stripes for RF)]. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05 versus Cc1+/+, †P ≤ 0.05 Cc1−/−xliver+ versus Cc1−/− mice/treatment group and ‡P ≤ 0.05 Cc1−/− versus others/treatment group. (B) Western analysis of lysates from aortae was performed to assess insulin receptor protein level (Ib: α-IRβ) and phosphorylation (Ib: α-pIRβ). The lower half of the gel was used to immunoblot with α-Tubulin antibody for protein normalization. (D–G) Lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against phosphorylated (p) Akt (D), eNOS (E), Foxo1 (F) and MAPkinase (G) (top gels), and with antibodies against the proteins to control for loading (lower gels). (B) Some aliquots were subjected to immunoprecipitation (Ip) with α-IRS1 antibody followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against phosphor-IRS1 (pIRS1, top gel), IRβ (middle gel), or IRS1 (bottom gel). (H) Other aortic lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (Ip) with α-Shc antibody followed by immunoblotting (Ib) with antibodies against phospho-CEACAM1 (pCC1, top gel), IRβ (middle gel) or Shc (lower gel). The apparent molecular weight (kDa) is indicated at the right hand-side of each gel. Gels represent 2 separate experiments performed on different mice/genotype/treatment.