Fig. 6. Assessment of efficacy of subconjunctival gel treatment by representing the parameters as clinical scores.
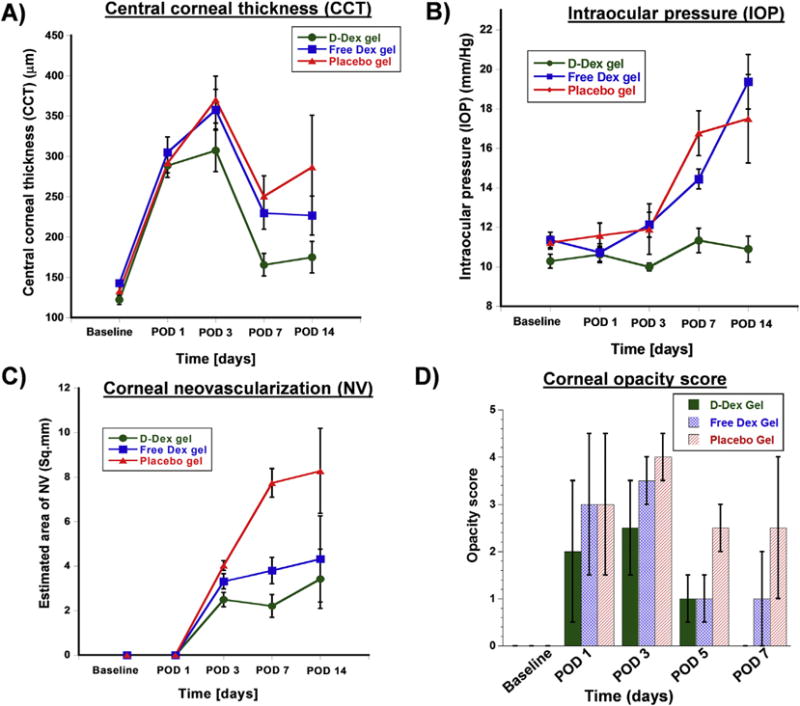
A) Central corneal thickness (CCT) measurements obtained by optical coherence tomography. All groups had an initial increase in CCT due to the alkali burn, however the D-Dex group gel group (the green line) had the best outcome with the lowest CCT. B) Intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements demonstrate a relatively stable IOP in the D-Dex gel group, whereas the free-Dex gel group and the positive controls have a gradual increase in IOP over the study period. C) Qualitative estimated area of neovascularization: neovascularization was first observed at post-operative day 3, and the least amount of corneal neovascularization was observed in the D-Dex gel group. D) Corneal opacity scores: The median opacity score of the D-Dex gel group at post-operative day 14 is zero. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
