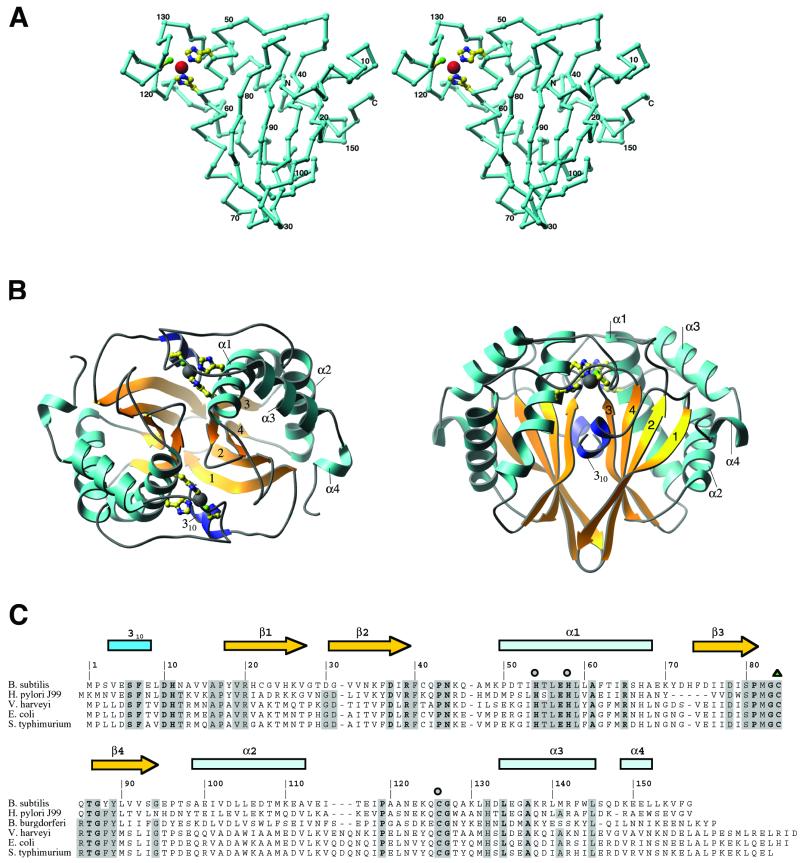
Figure 1.
The structure of LuxS. (A) A stereodrawing of the monomer fold, oriented to show the topology of the sheet and the zinc-binding site. The assignments of residues to various secondary structures are shown in C. Zn is represented as a large sphere, and the protein ligands, His-54, His-58, and Cys-126, are drawn in ball-and-stick mode. The crystallographic 2-fold axis relating the monomer units is approximately vertical in this view. A and panel B were composed with the RIBBONS program (32). (B) The dimer of LuxS in two orientations, viewed down the 2-fold axis (Left) and perpendicular to the 2-fold axis (Right). The helices are labeled and sheet strands are numbered according to their order in the sequence. (C) Sequence alignments of LuxS proteins from selected organisms. Five representatives of the 26 sequences used for alignment are included here. Residues that are invariant in all 26 sequences are labeled in boldface; those that are conserved in at least 80% of the sequences are highlighted in gray. Metal ligands are denoted with circles, and oxidized cysteine is indicated by a triangle.