Fig. 5.
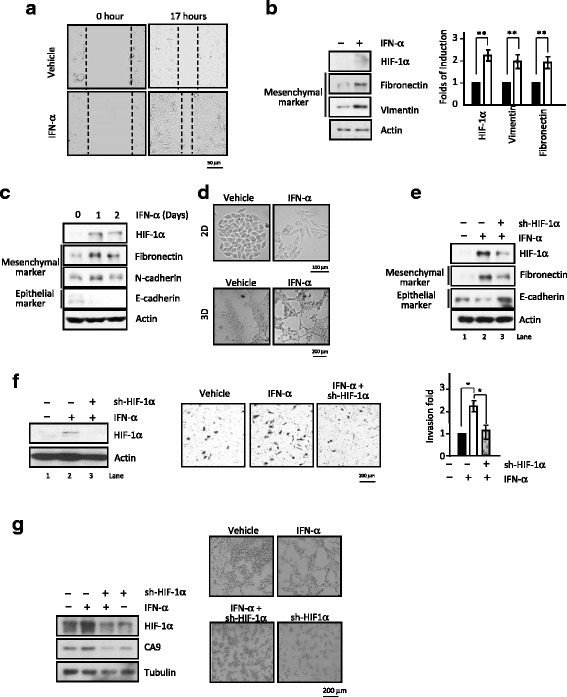
Funtional HIF-1α expression plays a critical role in IFN-α-stimulated tumorigenic propensities. a Wound-healing ability is increased upon IFN-α exposure. Gap images were captured under microscope at post-treatment time of 0 and 17 h. b-d IFN-α regulates protein expression of EMT genes, including up-regulation of mesenchymal marker proteins (b, quantitation data, right panel) and decrease in epithelia marker E-cadherin (c), and promotes EMT ability (d). The images of cellular morphology upon IFN-α stimulation were changed. In the 2D assay (the upper panel), cells were treated with or without IFN-α for 5–6 days and in the 3D assay (the lower panel), the vasculogenic mimicry of cells with or without IFN-α for 24 h. The images of both of them were observed under the phase contrast microscope. e-g The elevated expression of fibronectin expression, reduced E-cadherin expression (e), enhanced invasion activity (f, quantitation data, right panel) and increased vasculogenic mimicry (g; quantitation data, right panel) caused by the IFN-α treatment all are mediated through up-regulation of functional HIF-1α. *, P < 0.05 (g) The IFN-α-induced higher HIF-1α and downstream gene CA9 expression and knockdown of HIF-1α (left panel), totally block the expression of them and the destruction of tubule formation (right panel).The corresponding levels of HIF-1α after IFN-α treatment and/or sh-HIF-1α knockdown were determined by immunoblotting analysis and shown (e, top column; f-g, left panels).*,P < 0.05
