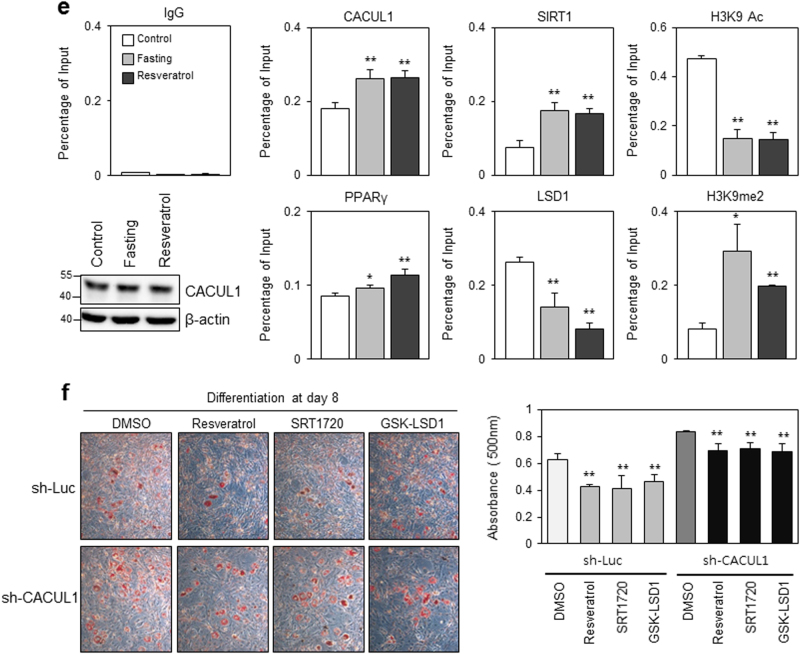
Fig. 5. CACUL1 reciprocally regulates SIRT1 and LSD1 for epigenetic repression of PPARγ.
a Cooperation of CACUL1 and SIRT1 to mediate PPARγ repression. HEK293 cells were transfected as indicated and were subjected to extraction for luciferase assays. Data indicate means±SD from three independent experiments (**P < 0.01). b Effect of LSD1 on PPARγ activation. Transfections and luciferase assays were performed as indicated (**P < 0.01). c Negative effect of CACUL1 on LSD1-enhanced PPARγ activity. (*P < 0.05). d Effect of CACUL1 depletion on H3K9 modifications during adipogenesis. Stable 3T3-L1 cells depleted of CACUL1 were subjected to differentiation for 8 days and chromatin IP (ChIP) assays using a primer set specific for the distal PPARγ-response site within the aP2 promoter and the indicated antibodies (H3K9ac and H3K9me, acetylation and demethylation at lysine 9 of histone H3, respectively). Data indicate means±SD from three independent experiments (*P < 0.05) (**P < 0.01). e Effect of fasting and resveratrol. After culturing undifferentiated 3T3-L1 cells in low-glucose DMEM (5.5 mm glucose; fasting condition) or treating with resveratrol (25 μm) for 24 h, ChIP assays were performed using the indicated antibodies. Data indicate means±SD from three independent experiments (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). CACUL1 expression is displayed by WB under these conditions. f Effect of resveratrol, SRT1720, or GSK-LSD1 treatment on adipogenesis under CACUL1-depleted conditions. CACUL1-depleted 3T3-L1 stable cells were treated with SIRT1 activators (resveratrol, 25 μm; SRT1720, 2.5 μm) or an LSD1 inhibitor (GSK-LSD1, 25 μm) and subjected to differentiation for 8 days. Lipid accumulation was visualized and measured as described (**P < 0.01)