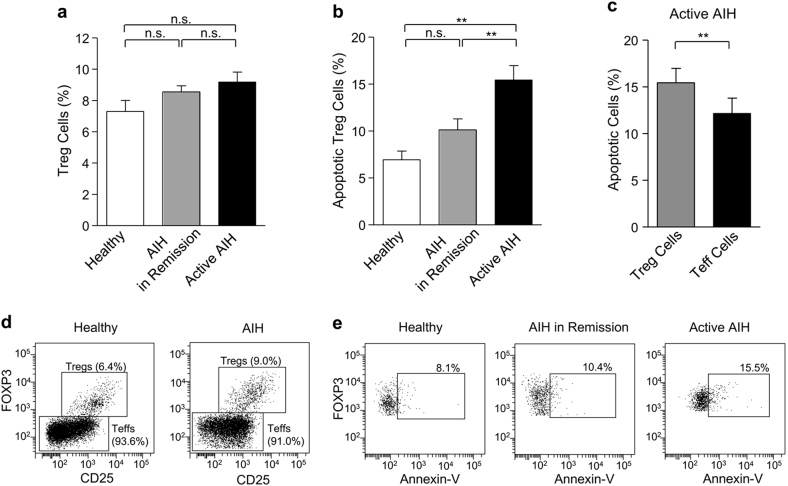
Fig. 1.
a Flow cytometric assessment of the percentage of CD4+CD25highCD127low/-FOXP3+ (T regulatory) cells among all CD4+ T cells in healthy subjects (n = 15) and patients with AIH in remission (n = 57) or active AIH (n = 42). b Analyses of the percentage of apoptotic (annexin-V-positive) Treg cells among the T regulatory cell population in healthy persons (n = 15) and AIH patients with (n = 57) or without (n = 42) biochemical remission. c Comparison of the percentage of apoptotic regulatory with apoptotic effector (CD4+CD25low/-FOXP3−) T cells in patients with active AIH (n = 42). d Representative flow cytometry of a healthy individual (left panel) and a patient with AIH (right panel) indicating the percentage of regulatory and effector T cells among CD4+ T cells. e Representative flow cytometry of a healthy individual (left panel), a patient with AIH in remission (middle panel) and a patient with active AIH (right panel) indicating the percentage of apoptotic Tregs among Treg cell population. Data represent means ± SEM; statistical analyses were performed by Mann–Whitney’s U-test (Fig. 1a, b) or Wilcoxon test (Fig. 1c). **p < 0.01; n.s. = not significant. Patient characteristics: AIH patients with biochemical remission had normal aminotransferase levels (AST 27.8 ± 1.0 U/L; ALT 23.9 ± 1.0 U/L), whereas in patients with active AIH the levels were increased (AST 81.0 ± 23.2 U/L; ALT = 92.1 ± 13.0 U/L). Patients with/without biochemical remission were positive for anti-nuclear (ANA), smooth-muscle (SMA), soluble-liver-antigens (SLA) or liver/kidney microsomal type-1 (LKM-1) antibodies in 56.1/66.7%, 33.3/50.0%, 17.5/11.9% and 10.5/9.5% of the cases. Viral hepatitis A-E was excluded. At the time of investigation, 88% (50/57) of the patients with and 95% (40/42) of the patients without remission received standard immunosuppressive therapy. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hannover Medical School.