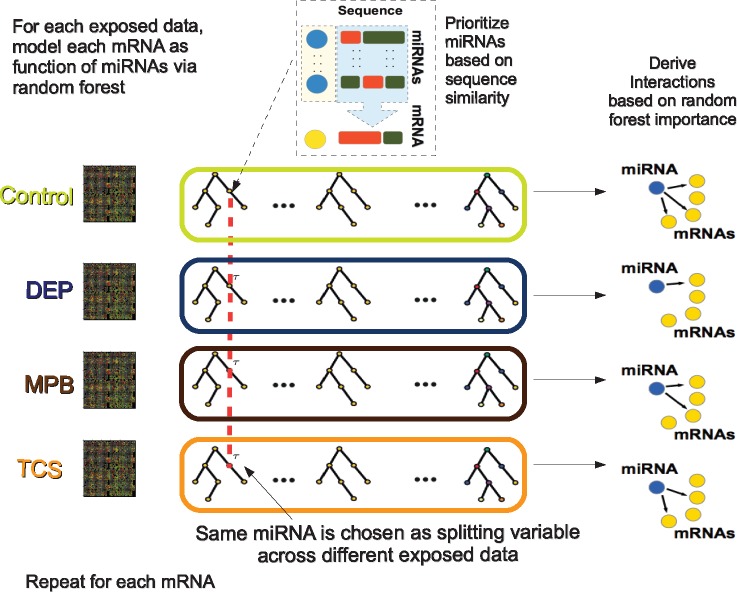
Fig. 1.
Joint Random Forest with iRafNet sampling scheme. For each exposure condition, model the expression of mRNAs as function of the expression of miRNAs via random forest. At each node, sample miRNAs prioritizing those present in TargetScan (Agarwal et al., 2015). Following JRF model (Petralia et al., 2016), the four random forest tree ensembles (Control, DEP, MPB and TCS) use the same splitting variables (miRNAs) to build trees. In this way we achieve borrowing information across them. This procedure is repeated for each mRNA and, then, interactions are ranked based on random forest importance scores